STRENGTHENING THE HEALTH CARE SYSTEM ACCORDING TO THE FOUR PRINCIPLES OF BHĀVANĀ TO SUPPORT THE AGING SOCIETY
Keywords:
Strengthening, Health Care System, Four Principles of Bhāvanā, Senior CitizensAbstract
Background and Objectives: Taking care of the health of the senior citizens is an important matter. Family members play a very important role in caring for the senior citizens. They must understand the problems in order to take care of the health and environment of the senior citizens correctly and appropriately. In addition, applying the four principles of Bhāvanā as a guideline to support the aging society will help the senior citizens to be happy, have a better mental state, and be able to rely on themselves. The objectives of this research article are to study the health care system to support the aging society and apply the four principles of Bhāvanā in health care to support the aging society.
Methodology: The study employed a qualitative research method by collecting data from related documents and in-depth interviews. Key informants included two scholar monks, two representatives from Hospital, two Village Health Volunteers (VHV), two temple volunteers, four senior citizens, and four caregivers, with a total of sixteen people.
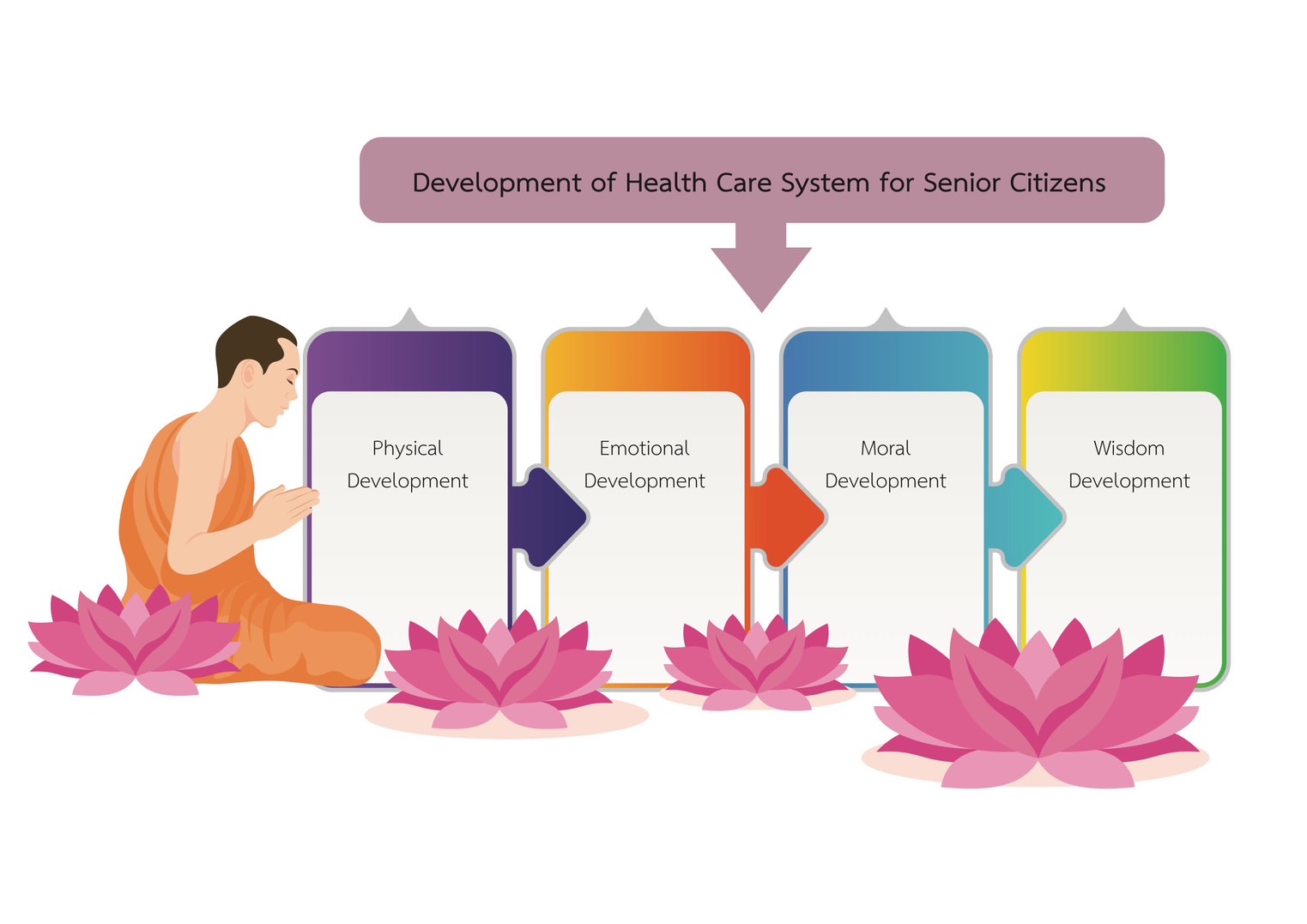
Main Results: The study results indicated that: 1) Health care system to support the aging society consisted of creating a network for healthcare systems to the senior citizens by creating a joint plan with the sub-district health promoting hospital, community, and senior citizens. The potential development of the health care network for senior citizens was conducted by workshop meetings to continuously follow up on the health care network for them. The establishment of schools for senior citizens was conducted through a meeting to appoint a committee to operate the care of senior citizens. It included network partners operating under the concept of promoting a lifelong learning process. Training to provide knowledge to caregivers of the senior citizens was a training program for caregivers. The senior citizen's caregivers were the mainstays to care for, follow up with, and visit senior citizens who were homebound and bedridden. The supervisor team provided supervision, evaluated performance, and organized a forum to exchange knowledge; and 2) The application of the four principles of Bhāvanā in health care to support the aging society consisted of physical, moral, emotional, and wisdom development. For physical development, the senior citizens developed themselves through physical awareness by considering factors that affected health. For moral development, the senior citizens developed themselves by adjusting behavior to promote their health by using healthcare to create a healthy society. For emotional development, the senior citizens developed themselves by making their minds comfortable and being kind to community members. For wisdom development, the senior citizens developed themselves through continuous learning by acknowledging and passing on knowledge to community members.
Involvement to Buddhadhamma: This research article is involved Applied Buddhism within the group of Buddhism for social benefits by applying the four principles of Bhāvanā for strengthening the aging society includes; physical development, which means having a supportive relationship for the physical environment of the senior citizens to have good physical health; moral development, which means having a supportive relationship with maintaining morality; emotional development, which means strengthening knowledge, thoughts, and understanding by developing a calm mind; and wisdom development, which means the search for knowledge of the senior citizens is always increasing.
Conclusions: Health care to support the aging society applied the four principles of Bhāvanā to help senior citizens be happy and able to rely on themselves. It started when senior citizens developed healthcare behaviors. Senior citizens maintained good health, were kind, and helped the community and society. They organized activities to promote the health of the senior citizens and the community in unity. They developed their comfort through continuous learning and inherited knowledge to community members.
References
Aekplakorn, W. (2014). The 5th Report of National Health Examination Survey B.E. 2557 (2014). Health Systems Research Institute.
Boonmee, S. (2019). Development of an Elderly Care Model with Participation of Community Network in Ban Nonphuey Tambol Health Promoting Hospital, Sanom District, Surin Province. Academic Journal of Community Public Health, 5(4), 38-49.
Boukeaw, P. & Teungfung, R. (2016). Health Care and Health Status of Thai Aging. Journal of the Association of Researchers, 21(2), 94-109.
Cronbach, L. J. (1990). Essentials of Psychological Testing (5th ed.). Harper Collins Publishers.
Homsombat, P., Phrabaidika Suphot Tabaselo, Fangkham, B. & Sornsakda, S. (2021). Elderly School: Enhancing Potentials of Elderly in Aging Society. Journal of Educational Innovation and Research, 6(2), 540-551.
Institute for Population and Social Research. (2019). Thai Health Report B.E. 2562 (2019). Institute for Population and Social Research.
Ministry of Social Development and Human Security. (2018). Department of Older Persons Strategy for 20 Years B.E. 2561-2580 (2018-2037). Samlada Printing.
Phrakru Suthee Kumpeerayarn. (2019). A Study on Guidelines for the Development Way of the Quality of Life for the Elder in Accordance with the Bhavana 4: Case study of Elder in Ban Huai Hoi, That Thong Sub-District, Phu Khiao District, Chaiyaphum Province. Journal of Graduate MCU Khonkaen Campus, 6(1), 58-72.
Piewsri, S. (2020). The Development of Health Care Behaviors of the Elderly by Using the 4 Bhavana Principles in Nong Phueng Subdistrict, Saraphi District, Chiang Mai Province. [Unpublished master's dissertation]. Mahachulalongkornrajavidyalaya University.
Taburee, W. (2016). Health Care System of the Elderly in the Community Contacting Unit of Naresuan University Hospital. Naresuan University.
Thanakwang, K. & Soonthorndhada, K. (2006). Attribute of Active Ageing Among Older Persons in Thailand: Evidence from the 2002 Survey. Asia-Pacific Population Journal, 21(3), 113-135.
World Health Organization: WHO. (2002). Active Ageing: A Policy Framework. World Health Organization.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Journal of Buddhist Anthropology

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.








