เซนเซอร์กระดาษที่มีลักษณะคล้ายบาร์โค้ดสำหรับการตรวจวัดน้ำกระด้าง
Main Article Content
บทคัดย่อ
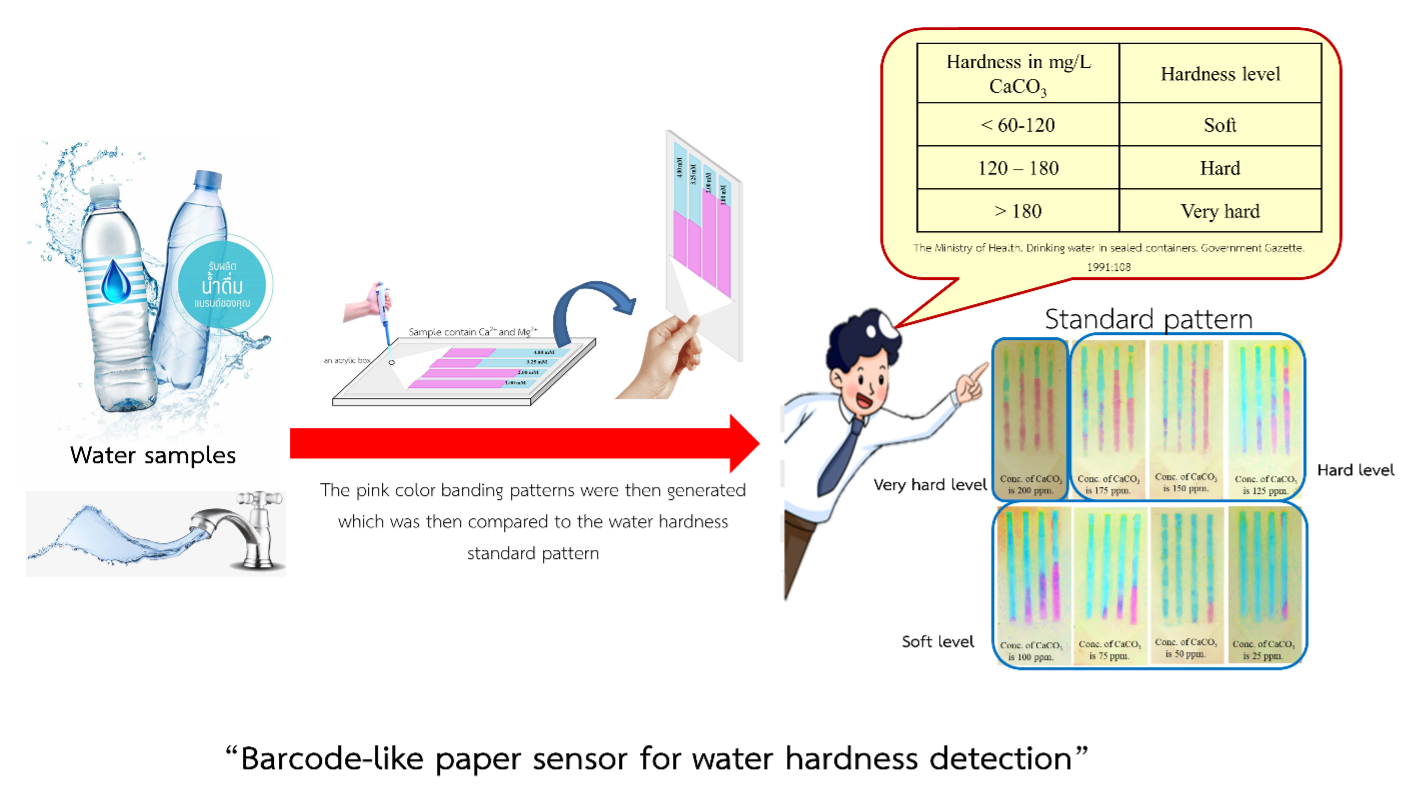
การวัดระดับความกระด้างของน้ำเป็นตัวแปรที่บ่งบอกถึงคุณภาพของน้ำ ซึ่งใช้การไทเทรตสารประกอบเชิงซ้อนเป็นวิธีมาตรฐาน อย่างไรก็ตามการใช้วิธีนี้อาจมีข้อจำกัดบางประการ เช่น การวิเคราะห์มีหลายขั้นตอน ใช้สารละลายปริมาณมาก (> 105 มิลลิลิตร) และต้องอาศัยผู้ที่มีทักษะในการทดลอง เพื่อลดข้อจำกัดดังกล่าว งานวิจัยนี้จึงนำเสนอเซนเซอร์กระดาษที่มีลักษณะคล้ายบาร์โค้ดที่ประดิษฐ์ขึ้นโดยเทคนิคการพิมพ์สกรีนด้วยไข ประกอบด้วยแถบการตรวจวัดรูปสี่เหลี่ยมผืนผ้า 4 ช่อง (แต่ละแถบมีขนาด 0.3 x 5.0 เซนติเมตร) และแถบสามเหลี่ยมด้านบนคือบริเวณหยดตัวอย่าง (มีขนาด 1.9 เซนติเมตร สำหรับความสูง x 2.9 เซนติเมตรสำหรับฐาน) จากนั้นหยดสารละลายผสมระหว่าง ไดโซเดียม เอทิลีนไดเอมีนเตตระอะซีติกแอซิด และอินดิเคเตอร์ อิริโอโครม แบลค ที (EDTA-EBT) ที่มีความเข้มข้นของ EDTA ที่แตกต่างกันในแต่ละแถบใน N-cyclohexyl amino-propanesulfonic acid (CAPs) บัฟเฟอร์ pH 10.5 ปริมาตร 40.00 ไมโครลิตร เคลือบลงบนบริเวณตรวจวัด เมื่อหยดมาตรฐานแคลเซียมคาร์บอเนตหรือสารละลายตัวอย่างที่มีแคลเซียมหรือแมกนีเซียมปริมาตร 120.00 ไมโครลิตรลงบนบริเวณดังกล่าว จากนั้นไม่กี่นาทีจะปรากฎแถบสีชมพูบนพื้นหลังสีน้ำเงินบนเซนเซอร์กระดาษ ซึ่งสามารถกำหนดรูปแบบการตรวจวัดมาตรฐานสำหรับการตรวจวัดความกระด้างของน้ำอยู่ที่ช่วง 25-200 มิลลิกรัมต่อลิตร (สามารถแยกความละเอียดได้ 25 มิลลิกรัมต่อลิตร) และสามารถอ่านค่าความเข้มข้นของระดับความกระด้างของน้ำเทียบต้นแบบแถบการตรวจวัดมาตรฐานได้ด้วยตาเปล่า ดังนั้นเซนเซอร์กระดาษที่มีลักษณะคล้ายบาร์โค้ดจึงสามารถใช้งานได้จริงสำหรับการวิเคราะห์เชิงกึ่งปริมาณ นอกจากนี้ระบบยังแสดงความทนต่อไอออนรบกวนต่าง ๆ ในตัวอย่างน้ำและการประยุกต์กับตัวอย่างจริงให้ผลการวิเคราะห์ที่ไม่แตกต่างกับผลการวิเคราะห์ที่ได้จากการไทเตรตเชิงซ้อนแบบเดิม
Article Details
วารสารวิทยาศาสตร์และวิทยาศาสตร์ศึกษา (JSSE) เป็นผู้ถือลิสิทธิ์บทความทุกบทความที่เผยแพร่ใน JSSE นี้ ทั้งนี้ ผู้เขียนจะต้องส่งแบบโอนลิขสิทธิ์บทความฉบับที่มีรายมือชื่อของผู้เขียนหลักหรือผู้ที่ได้รับมอบอำนาจแทนผู้เขียนทุกนให้กับ JSSE ก่อนที่บทความจะมีการเผยแพร่ผ่านเว็บไซต์ของวารสาร
แบบโอนลิขสิทธิ์บทความ (Copyright Transfer Form)
ทางวารสาร JSSE ได้กำหนดให้มีการกรอกแบบโอนลิขสิทธิ์บทความให้ครบถ้วนและส่งมายังกองบรรณาธิการในข้อมูลเสริม (supplementary data) พร้อมกับนิพนธ์ต้นฉบับ (manuscript) ที่ส่งมาขอรับการตีพิมพ์ ทั้งนี้ ผู้เขียนหลัก (corresponding authors) หรือผู้รับมอบอำนาจ (ในฐานะตัวแทนของผู้เขียนทุกคน) สามารถดำเนินการโอนลิขสิทธิ์บทความแทนผู้เขียนทั้งหมดได้ ซึ่งสามารถอัพโหลดไฟล์บทความต้นฉบับ (Manuscript) และไฟล์แบบโอนลิขสิทธิ์บทความ (Copyright Transfer Form) ในเมนู “Upload Submission” ดังนี้
1. อัพโหลดไฟล์บทความต้นฉบับ (Manuscript) ในเมนูย่อย Article Component > Article Text
2. อัพโหลดไฟล์แบบโอนลิขสิทธิ์บทความ (Copyright Transfer Form) ในเมนูย่อย Article Component > Other
ดาวน์โหลด ไฟล์แบบโอนลิขสิทธิ์บทความ (Copyright Transfer Form)
เอกสารอ้างอิง
Betz, J., and Noll, C. (1950). Total‐hardness determination by direct colorimetric titration. Journal‐American Water Works Association, 42(1), 49-56.
Dungchai, W., Chailapakul, O., and Henry, C. S. (2011). A low-cost, simple, and rapid fabrication method for paper-based microfluidics using wax screen-printing. Analyst, 136(1), 77-82.
Jarujamrus, P., Malahom, N., Puchum, S., Meelapsom, R., Amatatongchai, M., Siripinyanond, A., Chairam, S., and Kulsing, C. (2018). Complexometric and argentometric titrations using thread-based analytical devices. Talanta, 183, 228-236.
Jarujamrus, P., Meelapsom, R., Naksen, P., Ditcharoen, N., Anutrasakda, W., Siripinyanond, A., Amatatongchai, M., and Supasorn, S. (2019). Screen-printed microfluidic paper-based analytical device (muPAD) as a barcode sensor for magnesium detection using rubber latex waste as a novel hydrophobic reagent. Analytica Chimica Acta, 1082, 66-77.
Karita, S., and Kaneta, T. (2016). Chelate titrations of Ca(2+) and Mg(2+) using microfluidic paper-based analytical devices. Analytica Chimica Acta, 924, 60-67.
Lindstrom, F., and Diehl, H. (1960). Indicator for the titration of calcium plus magnesium with (ethylenedinitrilo) tetraacetate. Analytical Chemistry, 32(9), 1123-1127.
Malahom, N., Jarujamrus, P., Meelapsom, R., Siripinyanond, A., Amatatongchai, M., and Chairam, S. (2017). Simple test kit based on colorimetry for quantification of magnesium content in natural rubber latex by miniaturized complexometric titration without using masking agent. Polymer Testing, 59, 160-167.
Martinez, A. W., Phillips, S. T., Butte, M. J., and Whitesides, G. M. (2007). Patterned paper as a platform for inexpensive, low-volume, portable bioassays. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 46(8), 1318-1320.
Namwong, P., Jarujamrus, P., Amatatongchai, M., and Chairam, S. (2018). Fabricating Simple Wax Screen-Printing Paper-Based Analytical Devices To Demonstrate the Concept of Limiting Reagent in Acid–Base Reactions. Journal of Chemical Education, 95(2), 305-309.
Wang, S., Ge, L., Song, X., Yu, J., Ge, S., Huang, J., and Zeng, F. (2012). Paper-based chemiluminescence ELISA: lab-on-paper based on chitosan modified paper device and wax-screen-printing. Biosens Bioelectron, 31(1), 212-218.
Yappert, M. C., & DuPre, D. B. (1997). Complexometric titrations: competition of complexing agents in the determination of water hardness with EDTA. Journal of Chemical Education, 74(12), 1422.