การสังเคราะห์และปรับปรุงคุณสมบัติของโคบอลต์ซิงค์อะลูมิเนียมเลเยอร์ดับเบิลไฮดรอกไซด์ด้วยอนุภาคแม่เหล็กระดับนาโนและไคโตซานสำหรับการดูดซับสีย้อมบริลเลียน กรีน
Main Article Content
บทคัดย่อ
วัสดุโคบอลต์ซิงค์อะลูมิเนียมเลเยอร์ดับเบิลไฮดรอกไซด์ ที่ปรับปรุงคุณสมบัติด้วยอนุภาคแม่เหล็กระดับนาโน
และไคโตซาน (Fe3O4CS@CoZnAl- Layered double hydroxides) ถูกเตรียมขึ้นสำหรับการดูดซับสารละลายสีย้อม
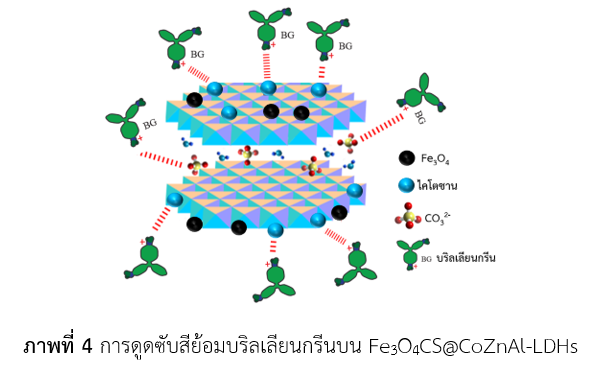
บริลเลียนท์ กรีน เพื่อแก้ไขปัญหาการปนเปื้อนของสีย้อมในน้ำ อนุภาคแม่เหล็กระดับนาโนช่วยให้การแยกตัวดูดซับออกจากสารละลายทำได้ง่าย และไคโตซานจะช่วยเพิ่มหมู่ไฮดรอกซิล สำหรับการสร้างอันตรกิริยากับสีย้อมบริลเลียน กรีน ที่มีประจุบวก จากการศึกษาโครงสร้างของวัสดุโดยเทคนิค XRD แสดงให้เห็นว่าหลังการปรับปรุงคุณสมบัติ วัสดุยังแสดงลักษณะโครงสร้างของเลเยอร์ดับเบิลไฮดรอกไซด์ และเมื่อทำการศึกษาการดูดซับสีย้อมที่ pH เท่ากับ 7 อุณหภูมิ 25 องศาเซลเซียส และความเข้มข้นเริ่มต้นของสีย้อมเป็น 20 ppm พบว่า Fe3O4CS@CoZnAl-LDHs แสดงเปอร์เซ็นต์การดูดซับที่ 99% ซึ่งมากกว่าวัสดุ CoZnAl-LDHs ที่สามารถดูดซับสีย้อมได้เพียง 58% กระบวนการดูดซับเข้าสู่สมดุลที่เวลา 360 นาที นอกจากนี้ ผลการศึกษา
ไอโซเทอร์มของการดูดซับพบว่าสอดคล้องกับแลงเมียร์ไอโซเทอร์ม และจากผลการศึกษาจลนพลศาสตร์ แสดงถึงกระบวนการดูดซับนี้เป็นปฏิกิริยาอันดับสองเสมือน ตัวดูดซับที่สังเคราะห์ขึ้น แสดงคุณสมบัติที่ดีในการนำไปใช้สำหรับดูดซับสีย้อมที่ปนเปื้อนในน้ำได้
Article Details

อนุญาตภายใต้เงื่อนไข Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
วารสารวิทยาศาสตร์และวิทยาศาสตร์ศึกษา (JSSE) เป็นผู้ถือลิสิทธิ์บทความทุกบทความที่เผยแพร่ใน JSSE นี้ ทั้งนี้ ผู้เขียนจะต้องส่งแบบโอนลิขสิทธิ์บทความฉบับที่มีรายมือชื่อของผู้เขียนหลักหรือผู้ที่ได้รับมอบอำนาจแทนผู้เขียนทุกนให้กับ JSSE ก่อนที่บทความจะมีการเผยแพร่ผ่านเว็บไซต์ของวารสาร
แบบโอนลิขสิทธิ์บทความ (Copyright Transfer Form)
ทางวารสาร JSSE ได้กำหนดให้มีการกรอกแบบโอนลิขสิทธิ์บทความให้ครบถ้วนและส่งมายังกองบรรณาธิการในข้อมูลเสริม (supplementary data) พร้อมกับนิพนธ์ต้นฉบับ (manuscript) ที่ส่งมาขอรับการตีพิมพ์ ทั้งนี้ ผู้เขียนหลัก (corresponding authors) หรือผู้รับมอบอำนาจ (ในฐานะตัวแทนของผู้เขียนทุกคน) สามารถดำเนินการโอนลิขสิทธิ์บทความแทนผู้เขียนทั้งหมดได้ ซึ่งสามารถอัพโหลดไฟล์บทความต้นฉบับ (Manuscript) และไฟล์แบบโอนลิขสิทธิ์บทความ (Copyright Transfer Form) ในเมนู “Upload Submission” ดังนี้
1. อัพโหลดไฟล์บทความต้นฉบับ (Manuscript) ในเมนูย่อย Article Component > Article Text
2. อัพโหลดไฟล์แบบโอนลิขสิทธิ์บทความ (Copyright Transfer Form) ในเมนูย่อย Article Component > Other
ดาวน์โหลด ไฟล์แบบโอนลิขสิทธิ์บทความ (Copyright Transfer Form)
เอกสารอ้างอิง
Azizian, S. and Eris, S. (2021). Chapter 6 - Adsorption isotherms and kinetics. Interface Science and Technology, 33, 445-509.
Kant, R. (2012). Textile dyeing industry an environmental hazard. Natural Science, 4(1), 22-26.
Lei, S., Wang, S., Gao, B., Zhan, Y., Zhao, O., Jin, S., Song, G., Lyu, X., Zhang, Y., and Tang, Y. (2020). Ultrathin dodecyl-sulfate-intercalated Mg-Al layered double hydroxide nanosheets with high adsorption capability for dye pollution. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 577, 181-190.
Lu, L., Li, J., Ng, D. H. L., Yang, P., Song, P., and Zuo, M. (2017). Synthesis of novel hierarchically porous Fe3O4@MgAl–LDH magnetic microspheres and its superb adsorption properties of dye from water. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 46, 315-323.
Rodríguez, D., L., Vicent, B. M., Núñez, J. J., Aracil, M. B., and Belda, E. B. (2021). Uses of Nanoclays and Adsorbents for Dye Recovery: A Textile Industry Review. Applied Sciences, 11(23), 11422-11449.
Saghir, S., Fu, E., and Xiao, Z. (2020). Synthesis of CoCu-LDH nanosheets derived from zeolitic imidazole framework-67 (ZIF-67) as an efficient adsorbent for azo dye from waste water. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 297, 110010.
Sahoo, T. R. and Prelot, B. (2020). Nanomaterials for the Detection and Removal of Wastewater Pollutants. Amsterdam: Elsevier
Saleh, T. A. (2022). Chapter 3 - Kinetic models and thermodynamics of adsorption processes: classification, Interface Science and Technology, 34, 65-97.
Wang, H., Li, Z., Yahyaoui, S., Hanafy, H., Seliem, M. K., Petriciolet, A. B., Dotto, G. L., Sellaoui, L., and Li, Q. (2020). Effective adsorption of dyes on an activated carbon prepared from carboxymethyl cellulose: Experiments, characterization and advanced modelling. Chemical Engineering Journal, 417, 2816.
Zubieta, C., Sierra, M. B., Morini, M. A., Schulz, P. C., Albertengo, L., and Rodríguez, M. S. (2008). The adsorption of dyes used in the textile industry on mesoporous materials. Colloid and Polymer Science, 286, 377–384.