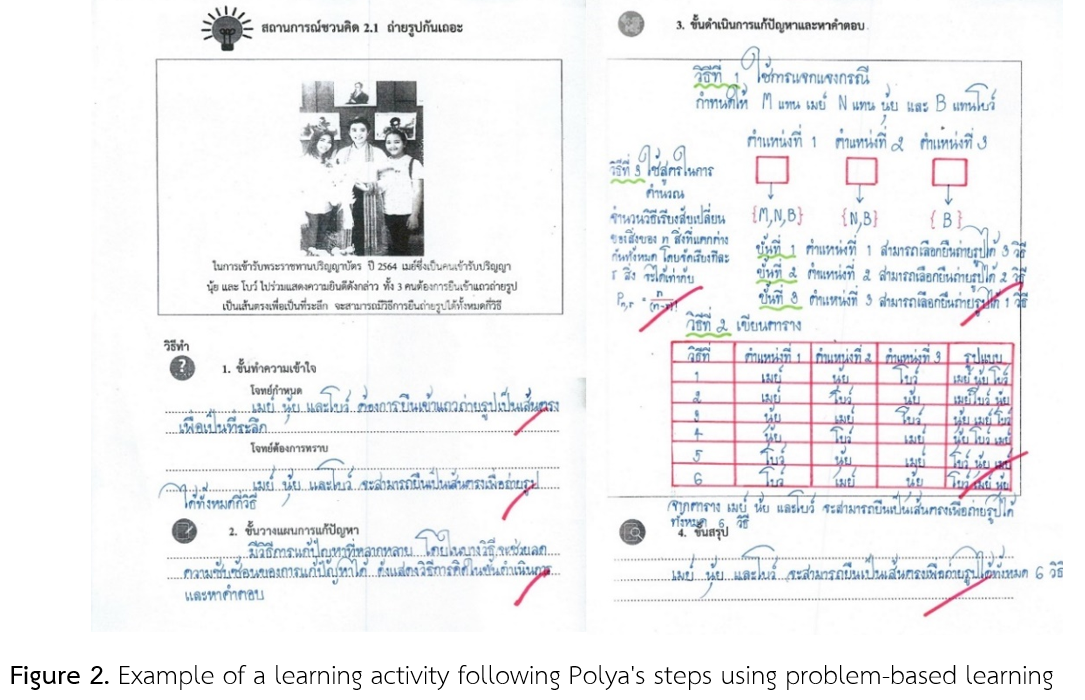
การพัฒนาทักษะการแก้ปัญหาทางคณิตศาสตร์ตามขั้นตอนของโพลยา เรื่อง หลักการนับเบื้องต้น ด้วยการจัดการเรียนรู้โดยใช้ปัญหาเป็นฐาน ของนักเรียนชั้นมัธยมศึกษาปีที่ 5
Main Article Content
บทคัดย่อ
การวิจัยครั้งนี้มีวัตถุประสงค์เพื่อ 1) เปรียบเทียบผลสัมฤทธิ์ทางการเรียนและทักษะการแก้ปัญหาทางคณิตศาสตร์ตามขั้นตอนของโพลยาก่อนเรียนและหลังเรียนด้วยการจัดการเรียนรู้โดยใช้ปัญหาเป็นฐาน 2) เปรียบเทียบผลสัมฤทธิ์ทางการเรียนและทักษะการแก้ปัญหาทางคณิตศาสตร์ตามขั้นตอนของโพลยาหลังการจัดการเรียนรู้โดยใช้ปัญหาเป็นฐานกับเกณฑ์ร้อยละ 80 กลุ่มตัวอย่างเป็นนักเรียนชั้นมัธยมศึกษาปีที่ 5 โรงเรียนราชสีมาวิทยาลัย ภาคเรียน ที่ 1 ปีการศึกษา 2565 จำนวน 33 คน เครื่องมือที่ใช้ในการวิจัย ได้แก่ แผนการจัดการเรียนรู้โดยใช้ปัญหาเป็นฐาน แบบทดสอบวัดผลสัมฤทธิ์ทางการเรียน และแบบทดสอบวัดทักษะการแก้ปัญหาทางคณิตศาสตร์ วิเคราะห์ข้อมูลโดย ใช้ค่าร้อยละ ค่าเฉลี่ย ค่าส่วนเบี่ยงเบนมาตรฐาน และสถิติทดสอบ dependent t-test ผลการวิจัยพบว่า ผลสัมฤทธิ์ทางการเรียนและทักษะการแก้ปัญหาทางคณิตศาสตร์ตามขั้นตอนของโพลยาหลังเรียนสูงกว่าก่อนเรียนอย่างมีนัยสำคัญทางสถิติที่ระดับ .01 และผลสัมฤทธิ์ทางการเรียนและทักษะการแก้ปัญหาทางคณิตศาสตร์หลังการจัดการเรียนรู้โดยใช้ปัญหาเป็นฐานสูงกว่าเกณฑ์ร้อยละ 80 อย่างมีนัยสำคัญทางสถิติที่ระดับ .01
Article Details

อนุญาตภายใต้เงื่อนไข Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
วารสารวิทยาศาสตร์และวิทยาศาสตร์ศึกษา (JSSE) เป็นผู้ถือลิสิทธิ์บทความทุกบทความที่เผยแพร่ใน JSSE นี้ ทั้งนี้ ผู้เขียนจะต้องส่งแบบโอนลิขสิทธิ์บทความฉบับที่มีรายมือชื่อของผู้เขียนหลักหรือผู้ที่ได้รับมอบอำนาจแทนผู้เขียนทุกนให้กับ JSSE ก่อนที่บทความจะมีการเผยแพร่ผ่านเว็บไซต์ของวารสาร
แบบโอนลิขสิทธิ์บทความ (Copyright Transfer Form)
ทางวารสาร JSSE ได้กำหนดให้มีการกรอกแบบโอนลิขสิทธิ์บทความให้ครบถ้วนและส่งมายังกองบรรณาธิการในข้อมูลเสริม (supplementary data) พร้อมกับนิพนธ์ต้นฉบับ (manuscript) ที่ส่งมาขอรับการตีพิมพ์ ทั้งนี้ ผู้เขียนหลัก (corresponding authors) หรือผู้รับมอบอำนาจ (ในฐานะตัวแทนของผู้เขียนทุกคน) สามารถดำเนินการโอนลิขสิทธิ์บทความแทนผู้เขียนทั้งหมดได้ ซึ่งสามารถอัพโหลดไฟล์บทความต้นฉบับ (Manuscript) และไฟล์แบบโอนลิขสิทธิ์บทความ (Copyright Transfer Form) ในเมนู “Upload Submission” ดังนี้
1. อัพโหลดไฟล์บทความต้นฉบับ (Manuscript) ในเมนูย่อย Article Component > Article Text
2. อัพโหลดไฟล์แบบโอนลิขสิทธิ์บทความ (Copyright Transfer Form) ในเมนูย่อย Article Component > Other
ดาวน์โหลด ไฟล์แบบโอนลิขสิทธิ์บทความ (Copyright Transfer Form)
เอกสารอ้างอิง
Abdullah, N. I., Tarmizi, R. A. and Abu, R. (2010). The effects of problem-based learning on mathematics performance and affective attributes in learning statistics at Form Four Secondary Level. Procedia Social and Behavioral Sciences, 8, 370–376.
Cotic, M. and Zuljan, M. V. (2009). Problem-based instruction in mathematics and its impact on the cognitive results of the students and on affective-motivational aspects. Educational Studies, 35(3), 297–310.
Institute for the Promotion of Teaching Science and Technology. (2013). Measurement and evaluation in mathematics. (in Thai). Bangkok: SE-Education.
Khammanee, T. (2017). Teaching and learning formats: diverse options. (in Thai). (9th ed.). Bangkok: Chulalongkorn University Press.
Laolearndee, W. (2011). Learning management models and strategies to develop thinking skills. (in Thai). (7th ed.). Nakhon Pathom: Silpakorn University Printing House.
Nilaphan, M. (2012). Educational Research Methods. (in Thai). Nakhon Pathom: Silpakorn University Printing House.
Ounpomma, W. and Pavapuyanon, L. (2017). The Development of Mathematics Learning Activities Based on Constructivist Theory Emphasizing Polya’s Problem-Solving Processes On Probability for Mathayomsuksa 5. (in Thai). Journal of Education Graduate Studies Research, KKU, 11(4), 154–166.
Ransungneon, P. (2012). Causal factors affecting mathematical problem-solving abilities of Grade 9 students in Education Area Office 1. (in Thai). Master's thesis. Srinakharinwirot University.
Suwan, S. (2011). Development of fraction problem-solving abilities using Polya's problem-solving process for Grade 6 students at Lamphun Kindergarten School. (in Thai). Master's thesis. Chiang Mai: Chiang Mai University.
Thanwiset, N. and Keeratichamroen, W. (2018). A study of learning achievement on work and energy learning unit and problem solving ability of grade 10 students using problem based learning (PBL). (in Thai). Academic Services Journal, Prince of Songkla University, 29(2), 43–50.
The Ministry of Education. (2008). The Basic Education Core Curriculum B.E. 2551. (A.D. 2008). (in Thai). Bangkok: Kurusapa Ladprao Printing House.
The Office of the Secretary-General of the Education Council. (2017). The National Education Plan B.E. 2560-2579. (A.D. 2017-2036). (in Thai). Bangkok: Ministry of Education.