Application of Monte Carlo Simulation Technique to Design Reservoir Area: A Case Study for Nong-Bua Reservoir in Chiang Rai, Thailand
Main Article Content
Abstract
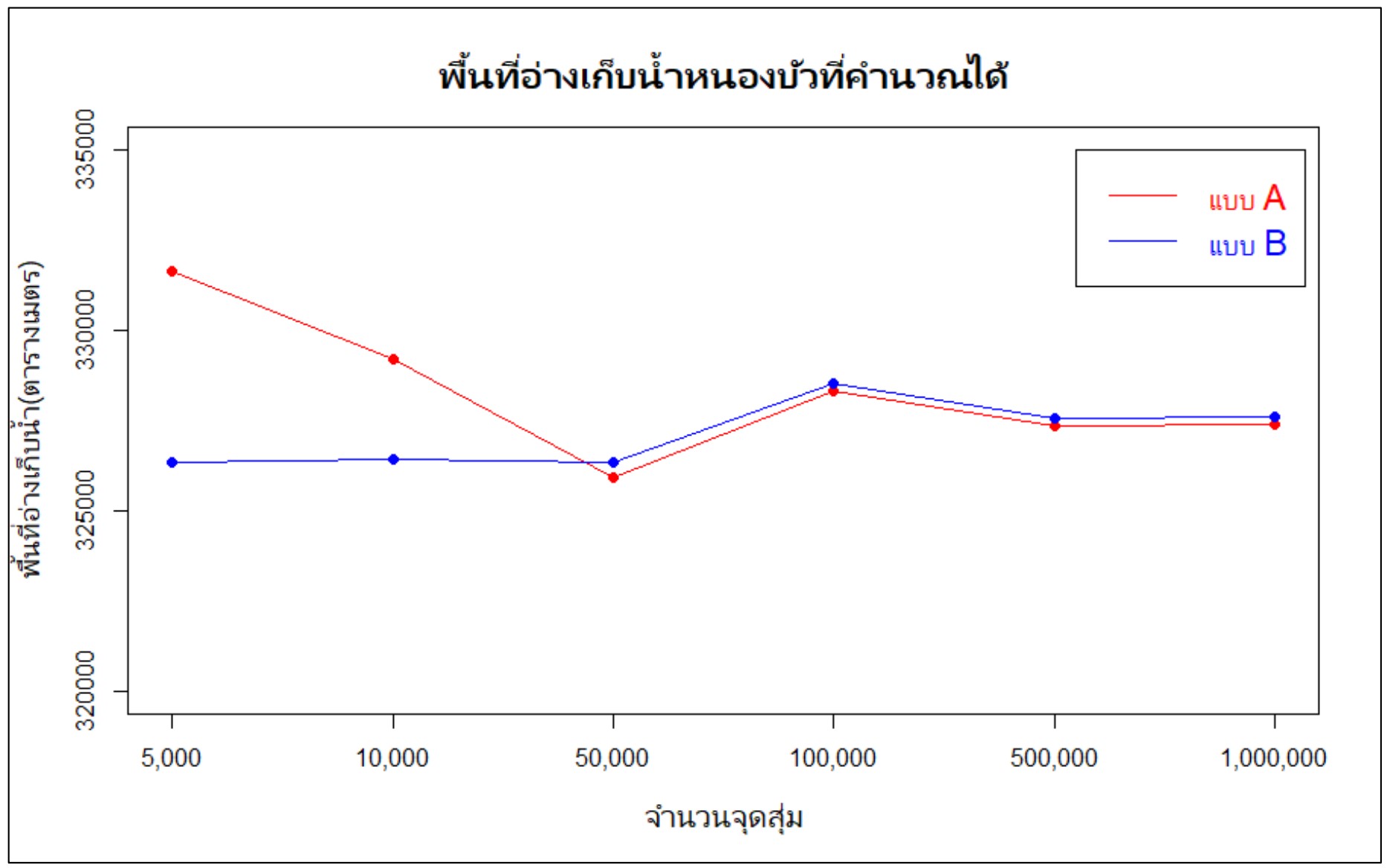
The purpose of this research was to apply the Monte Carlo technique to compare the appropriate method for estimation area of Nong-Bua Reservoir in the park of 80th Birthday Anniversary of Her Royal Highness Princess Srinagarindra, the Princess Mother at Chiang Rai Rajabhat University. We were using R program and satellite images for simulating reservoir area. The study revealed that the setting a rectangular frame close to the edge of Nong-Bua Reservoir (Type A) and the setting a rectangular frame with spacing at the edge of Nong-Bua Reservoir (Type B) can calculate the reservoir area similarly when specifying more than 50,000 random points. When specifying random points from 500,000 or more, it was found that the Nong-Bua Reservoir area calculated in both designs became stable. It was approximately 327,000 square meters or approximately 204 rai and both types gave the least calculation discrepancy when assigning 1,000,000 random points.
Article Details
References
กองอาคารสถานที่ มหาวิทยาลัยราชภัฏเชียงราย. (2565). สวนสมเด็จพระศรีนครินทร์. สืบค้นเมื่อ 10 ธันวาคม 2565 จาก https://buildings.crru.ac.th/suansomdej.php.
ณัฐพล โชติศรีศุภรัตน์. (2521). การทดลองเพื่อทำความเข้าใจวิธีมอนติคาร์โล (Monte Carlo method). สืบค้นเมื่อ 10 ธันวาคม 2565 จาก http://www.thaiphysoc.org/article/385/.
ประเสริฐ ไวยกา และ รวินท์นิภา บุดดี. (2022). การศึกษาความหลากหลายของแพลงก์ตอนพืช เพื่อเป็นดัชนีบ่งชี้คุณภาพน้ำในแหล่งน้ำของมหาวิทยาลัยราชภัฏเชียงราย. Journal of Science and Technology Phetchabun Rajabhat University, 2(1).
สำนักงานทรัพยากรน้ำที่ 1. (2565). สทภ.1 รอง อทน. ลงพื้นที่ติดตามความก้าวหน้าโครงการอนุรักษ์ฟื้นฟูหนองบัว พร้อมระบบกระจายน้ำด้วยพลังงานแสงอาทิตย์ จ.เชียงราย. สืบค้นเมื่อ 10 ธันวาคม 2565 จาก https://dwr.go.th/news_inside.php?news_id=108723.
สำนักงานเทศบาลตำบลบ้านดู่. (2560). รายงานการศึกษาตลาดสดเทศบาลตำบลบ้านดู่ อำเภอเมืองเชียงราย จังหวัดเชียงราย. สืบค้นเมื่อ 10 ธันวาคม 2565 จาก http://bandu.go.th/old/doc/
pdf.
Carmel Yohay, Paz Shlomit , Jahashan Faris , and Shoshanya Maxim. (2009). Assessing fire risk using Monte Carlo simulations of fire spread. Forest Ecology and Management, 1(257), 370-377.
Dirk P. Kroese. (2011). Monte Carlo Methods. An honors/graduate course on Monte Carlo Methods, Department of Mathematics, School of Mathematics and Physics, The University of Queensland.
F. Franza, P. D. Bates, J. C. Neal G. T. Aronica. (2012). Probabilistic evaluation of flood hazard in urban areas using Monte Carlo simulation. Hydrological Processes, 26(26), 3962-3972.
James Charalambous, Ataur Rahman, and Carroll Don. (2013). Application of Monte Carlo Simulation Technique to Design Flood Estimation: A Case Study for North Johnstone River in Queensland, Australia. Water Resour Manage (27), 4099–4111. From https:// doi.org/10.1007/s11269-013-0398-9.
Nicola Covre, Alessandro Luchetti, Matteo Lancini, Simone Pasinetti, Enrico Bertolazzi and Mariolino De Cecco. (2022). Monte Carlo-based 3D surface point cloud volume estimation by exploding local cubes faces. ACTA IMEKO, 11(2), 1-9.
Soleimani Hamed, Nasri Omid, Ghoochani Mahboobeh, Azhdarpoor Abooalfazl , Radfard Majid , and Dehghani Mansooreh . (2022). Groundwater quality evaluation and risk assessment of nitrate using monte carlo simulation and sensitivity analysis in rural areas of Divandarreh County, Kurdistan province, Iran. International Journal of Environmental Analytical Chemistry, 102(10), 2213-2231. doi:10.1080/03067319. 2020.1751147.
William Oberle. (2015). Monte Carlo Simulations: Number of Iterations and Accuracy. US Army Research Laboratory, ARL-TN-0684, JULY 2015.