The promotion of child development using Line chatbot and machine learning
Main Article Content
Abstract
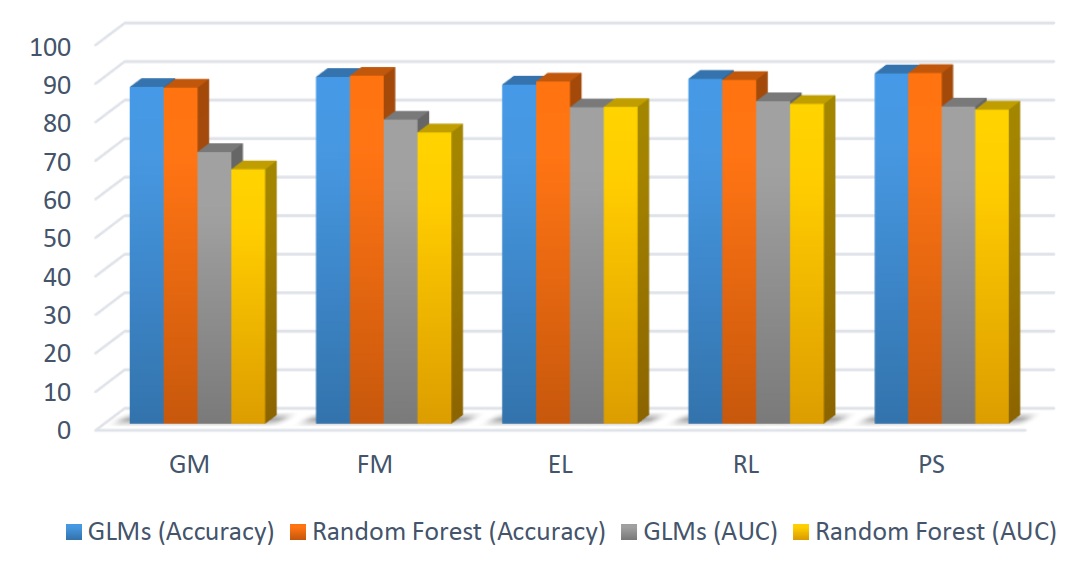
Promoting the development of children from birth to 5 years is essential because children's brains develop at the fastest rate. The brain creates billions of neural connections every second. Appropriate stimulation such as touching, talking and playing help promote brain cell connections, giving children a strong learning foundation. however, challenges such as overcrowding at hospitals and the COVID-19 pandemic have made it difficult for parents to access child development promotion services. This study utilizes the Early Childhood Development Assessment and Promotion Manual to evaluate the development of young children in five areas: Gross Motor (GM), Fine Motor (FM), Receptive Language (RL), Expressive Language (EL), and Personal and Social (PS). The objective of this research is to develop a chatbot on the LINE platform to facilitate child development promotion, aiming to alleviate the aforementioned challenges. The study employs Random Forest models and Generalized Linear Models (GLMs), trained using child development data collected from 2014 to 2019, with the RapidMiner Studio Educational Version 9.5.001 software. The performance of these models was evaluated based on Accuracy and Area Under the Curve (AUC). The findings indicate that the development of a chatbot for child development promotion significantly enhances the ease, convenience, and speed of parental child development assessments. The chatbot also enables real-time data collection. Furthermore, the results reveal that the Generalized Linear Model outperforms the Random Forest model in predictive efficiency.
Article Details
References
กระทรวงสาธารณสุข. (2023). คู่มือประเมินและส่งเสริมพัฒนาการเด็กกลุ่มเสี่ยง (Developmental Assessment For Intervention Manual: DAIM). Retrieved November 9, 2023, from คลังความรู้สุขภาพจิต กรมสุขภาพจิต website: https://dmh-elibrary.org/items/show/268
พิชชาพร คาทา, ประศาสตร์ บุญสนอง. (2564). แชทบอทสำหรับการบริการข้อมูลด้านสุขภาพ. การประชุมวิชาการเสนอผลงานวิจัยระดับชาติด้านวิทยาศาสตร์และเทคโนโลยี มหาวิทยาลัยราชภัฏจันทรเกษม ครั้งที่ 4.
คณะวิทยาศาสตร์ มหาวิทยาลัยราชภัฏจันทรเกษม.
สิริณัฏฐ์ โภคพัชญ์ภูเบศ, ชลิดา ธนัฐธีรกุล, สมสมร เรืองวรบูรณ. (2561). การพัฒนารูปแบบการส่งเสริมพัฒนาการเด็กในศูนย์พัฒนาเด็กเล็ก. วารสารวิทยาลัยพยาบาลบรมราชชนนี กรุงเทพ, 71–85.
อรพรรณ บุตรกตัญญู. (2542). การศึกษาความเข้าใจของผู้บริหาร และครูเกี่ยวกับการปฏิบัติที่เหมาะสมกับ พัฒนาการของเด็กวัยอนุบาล. มหาวิทยาลัยจุฬาลงกรณ์.
Andrea M. Austin, Ramkumar, N., Gladders, B., Barnes, J., Eid, M. A., Moore, K. O., … Goodney, P. P. (2022). Using a cohort study of diabetes and peripheral artery disease to compare logistic regression and machine learning via random forest modeling. BMC Medical Research Methodology. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12874-022-01774-8
DataReportal. (2019). DIGITAL 2019: THAILAND. Retrieved from www.datareportal.com website: https://datareportal.com/reports/digital-2019-thailand?fbclid=IwAR3I58JJuxvFofwBJ1K1Hc3Nv02yxHxpn1c9QvRhSrUwVVxZBc9wfbSIpLo
J. Li, Dada, A., Kleesiek, J., and Egger, J. (2023). ChatGPT in Healthcare: A Taxonomy and Systematic Review. MedRxiv. https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.03.30.23287899
Mohd. Sameer, and Santosh Kumar. (2023). AI Enabled NLP based Text to Text Medical Chatbot.