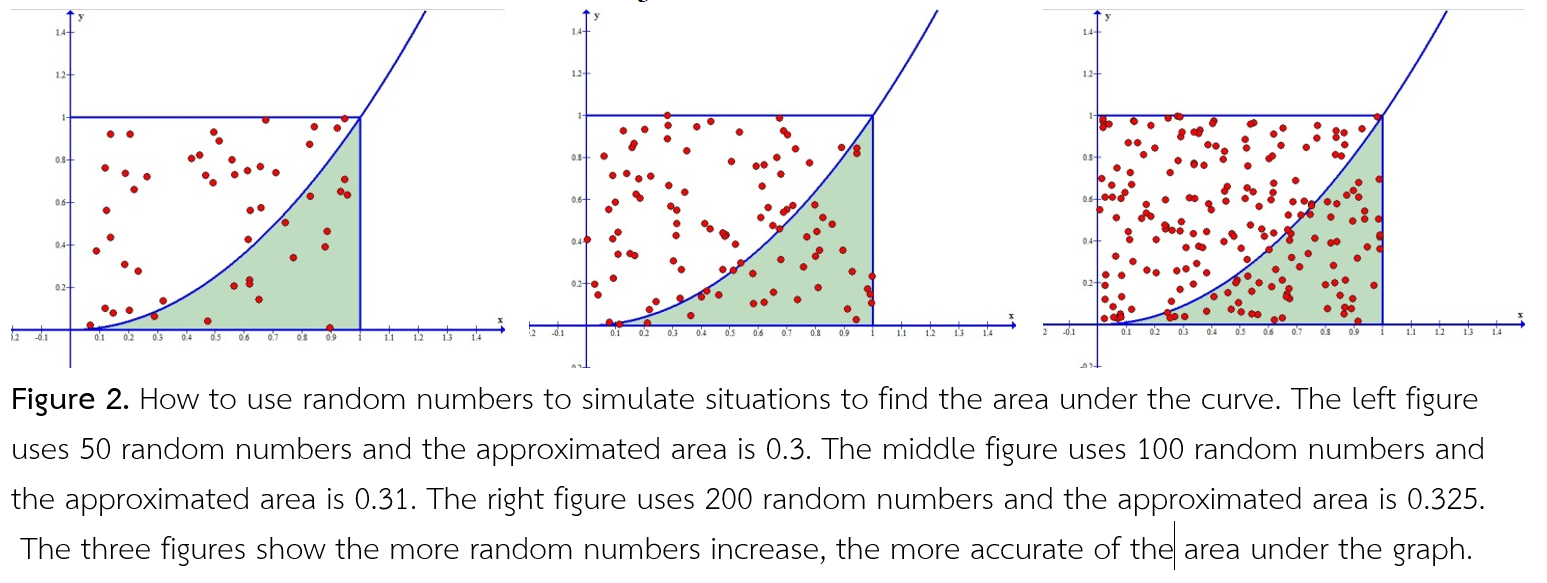
Using random numbers to simulate situations
Main Article Content
Abstract
Applications on mathematics can be used to explain in many phenomenon in both science and other areas called mathematical modeling. If such mathematical modeling can explain those phenomenon well and be accurate, using random numbers in order to simulate situations is one of important mathematical models and also widely used. In this paper, we present using random numbers to simulate determined and probability situations which are ease to understand. We apply the methods in real live situations, namely, warehouse problems. The results show the applications of mathematics in order to efficiently use in managements in many situations by using relevant mathematical models.
Article Details
The Journal of Science and Science Education (JSSE) retain the right of all articles published in JSSE. The coresponding author or the authorized person on behalf of the authors must send the complete Copyright Transfer Form to JSSE before any article get published in JSSE.
Copyright Transfer Form
The JSSE request the coresponding author or the authorized person on behalf of the authors upload the manuscript under the together with the Copyright Transfer Form under the supplementary data. The guidline for uploading both manuscript and Copyright Transfer Form is shown below:
1. Upload the manuscript in the sub-menu, Article Component > Article Text.
2. Upload the the Copyright Transfer Form in the sub-menu, Article Component > Other.
Download Copyright Transfer Form
References
Al-Harkan, I. and Hariga, M. (2007). A simulation optimization solution to the inventory continuous review problem with lot size dependent lead time. Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering, 32(2), 327-338.
Badri, M. A. (1999). A simulation model for multi-product inventory control management. Simulation, 72(1), 20-32.
Davis, E. R., Eckhause, J. M., Peterson, D. K., Pouy, M. R., Sigalas-Markham, S. M. and Volovoi, V. (2013). Exploring how hierarchical modeling and simulation can improve organizational resourcing decisions. In Proceedings of the Winter Simulation Conference: Simulation: Making Decisions in a Complex World (pp. 2496-2507). Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press.
Giordano, F. R., Fox, W. P. and Horton, S. B. (2013). A first course in mathematical modeling. Nelson Education.
Ižaríková, G. (2015). Process simulation and method of generating random numbers. International Scientific Journal about Simulation, 1(2), 1-4.
L'Ecuyer, P. (1990). Random numbers for simulation. Communications of the ACM, 33(10), 85-97.
Lee, E. and Farahmand, K. (2010). Simulation of a base stock inventory management system integrated with transportation strategies of a logistic network. In Proceedings of the Winter Simulation Conference (pp. 1934-1945). Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press.
Merkuryev, Y. A., Petuhova, J. J., Van Landeghem, R. and Vansteenkiste, S. (2002). Simulation-based analysis of the bullwhip effect under different information sharing strategies. In Proceedings of European Simulation Symposium (Vol. 299). Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press.
Metropolis, N. (1987). The beginning of the Monte Carlo method. Los Alamos Science, 15(584), 125-130.
Robinson, S. (1997). Simulation model verification and validation: increasing the users' confidence. In Proceedings of the Winter Simulation Conference (pp. 53-59). Washington, DC: IEEE Computer Society.