Development of Data Management and Scientific Interpretation Skills of Tenth Grade Students in Chemistry Subject through 5D Active Learning Management by Professional Learning Community
Main Article Content
Abstract
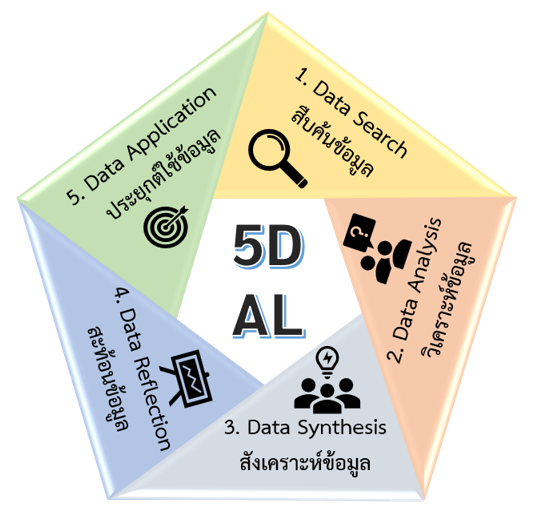
This research aimed to develop data management and scientific interpretation skills of tenth grade students in Chemistry through the 5D active learning management (Data search, Data analysis, Data synthesis, Data reflection and Data application) using the professional learning community process. The one group posttest only design was employed in this research. The sample was purposively selected from tenth grade students in the second semester of the 2024 academic year at a secondary school in Nakhon Ratchasima Province. The research instruments consisted of 17 5D active learning plans, worksheets and posttest of data management and scientific interpretation skills. The score data of worksheets and exit-tickets were analyzed by calculating the mean, standard deviation and percentage. The results of the research found that students had group and individual data management skills at an average score of 95.49 and 95.29 percent of the full score, respectively, while scientific interpretation skills had an average score of 94.52 and 90.53 percent of the full score, respectively, which were at a very good level. Learning through the 5D active process in 5 steps effectively promoted students’ analytical thinking and scientific reasoning processes. In particular, group activities and participatory assessments facilitated meaningful learning and enabled students to apply their knowledge.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
The Journal of Science and Science Education (JSSE) retain the right of all articles published in JSSE. The coresponding author or the authorized person on behalf of the authors must send the complete Copyright Transfer Form to JSSE before any article get published in JSSE.
Copyright Transfer Form
The JSSE request the coresponding author or the authorized person on behalf of the authors upload the manuscript under the together with the Copyright Transfer Form under the supplementary data. The guidline for uploading both manuscript and Copyright Transfer Form is shown below:
1. Upload the manuscript in the sub-menu, Article Component > Article Text.
2. Upload the the Copyright Transfer Form in the sub-menu, Article Component > Other.
Download Copyright Transfer Form
References
Becker, N. J. (2003). Google in perspective: Understanding and enhancing student search skills. New Review of Academic Librarianship, 9(1), 84-99.
Bowen, G. M. and Roth, W. M. (2005). Data and graph interpretation practices among preservice science teachers. Journal of Research in Science Teaching, 42(10), 1063-1088.
Chanchusakun, S. (2018). Concepts, principles and strategies of assessment for learning (in Thai). Journal of Educational Measurement Mahasarakham University, 24(1), 14-18.
Furtak, E. and Ruiz-Primo, M. (2008). Making students' thinking explicit in writing and discussion: An analysis of formative assessment prompts. Science Education, 92, 799-824.
Hogan, K. and Maglienti, M. (2001). Comparing epistemological underpinnings of students' and scientists' reasoning about conclusions. Journal of Research in Science Teaching, 38, 663-687.
Hu, H. W. and Chiu, C. H. (2024). The effect of using questioning strategies in scientific inquiry videos on elementary Students. Journal of Science Education and Technology, 33(6), 835-850.
Jeong, H., Songer, N. and Lee, S. Y. (2007). Evidentiary competence: Sixth graders' understanding for gathering and interpreting evidence in scientific investigations. Research in Science Education, 37(1), 75-97.
Kampetch, P., Sriharan, P. and Hirunsathaporn, W. (2021). The importance and techinques of data collection for 21th century researches (in Thai). Journal of Education Burapha University, 32(2). 1-12.
Kanari, Z. and Millar, R. (2004). Reasoning from data: How students collect and interpret data in science investigations. Journal of Research in Science Teaching, 41(7), 748-769.
Lai, M. K. and Hsiao, S. (2014). Developing data collection and management systems for decision-making: What professional development is required?. Studies in Educational Evaluation, 42, 63-70.
Lim, R. R. (2025). Impact of exit tickets on student achievement and learning experience in science. International Journal for Multidisciplinary Research 7(1), 1-8.
Makmun, M., Khoo, Y. Y. and Zakariya, Z. (2020). The gallery walk teaching and learning and its potential impact on students’ interest and performance. International Business Education Journal, 13(1), 17-22.
Masic, I., Jankovic, S. and Begic, E. (2019). PhD students and the most frequent mistakes during data interpretation by statistical analysis software. Studies in health technology and informatics, 262, 105-109.
Matzen, L., Divis, K., Haass, M. and Cronin, D. (2020). Variable Biases: A Study of Scientists’ Interpretation of Plot Types Commonly Used in Scientific Communication. United States: Sandia National Laboratories, University of California, Davis.
Pabchanda, S. (2024). Best practices of professional learning communities. Nakhon Ratchasima: Nakhon Ratchasima Rajabhat University.
Pangandaman, H., Datumanong, N., Mukattil, N., Hayudini, M. A., Abdulhan, M., Jilah, A. and Mercado, C. (2025). Effectiveness of mind mapping in the improvement of students academic performance: A systematic. Review. Cuestiones de Filosofía, 53, 1363-1375.
Penny, C. (2023). Students' Interpretation of Plot Types Commonly Used in Scientific Communication. Master's Thesis, Glasgow: University of Glasgow, Scotland.
Ramalli, E., Dinelli, T., Nobili, A., Stagni, A., Pernici, B. and Faravelli, T. (2023). Automatic validation and analysis of predictive models by means of big data and data science. Chemical Engineering Journal, 454, 140-149.
Roth, W. M. and Roychoudhury, A. (1993). The development of science process skills in authentic contexts. Journal of Research in Science Teaching, 30(2), 127-152.
Sakonthawat, P. and Pabchanda, P. (2021). The development of punctuality for eleventh grade students in chemistry with blended learning based on inquiry, social media, exit ticket and scorecard through lesson design by using professional learning community activity (in Thai). Journal of Science and Science Education, 4(2), 204-216.
Sawangmek, S. (2019). Promoting interpret data and evidence scientifically competency and attitude toward science through informal science camp. Proceedings of American Institute of Physics Conference (pp. 30-37). Maryland: American Institute of Physics.
Songer, N. B. and Linn, M. C. (1991). How do students' views of science influence knowledge integration? Journal of Research in Science Teaching, 28(9), 761-784.
Sriwanna, K. and Pabchanda, S. (2021). The development of analytical thinking skill and scientific minds in chemistry of tenth grade student by constructivism and collaborative learning (in Thai). Journal of Education Khon Kaen University, 44(2), 97-109.
The Institute for the Promotion of Teaching Science and Technology. (2025). PISA 2022 full report. Retrieved May 8, 2025, from Pisathailand: https://pisathailand.ipst.ac.th/pisa2022-fullreport
Xing, W., Lee, H. S. and Shibani, A. (2020). Identifying patterns in students’ scientific argumentation: content analysis through text mining using Latent Dirichlet Allocation. Educational Technology Research and Development, 68(5), 2185–2214.