การตรวจวัดเชื้อแบคทีเรียก่อโรคแบบรวดเร็วโดยใช้อนุภาคนาโนเหล็กออกไซด์ซุปเปอร์พาราแมกเนติกด้วยแมกนีโตอิมพีแดนซ์เซ็นเซอร์ความไวสูง: การศึกษาเบื้องต้น
Main Article Content
บทคัดย่อ
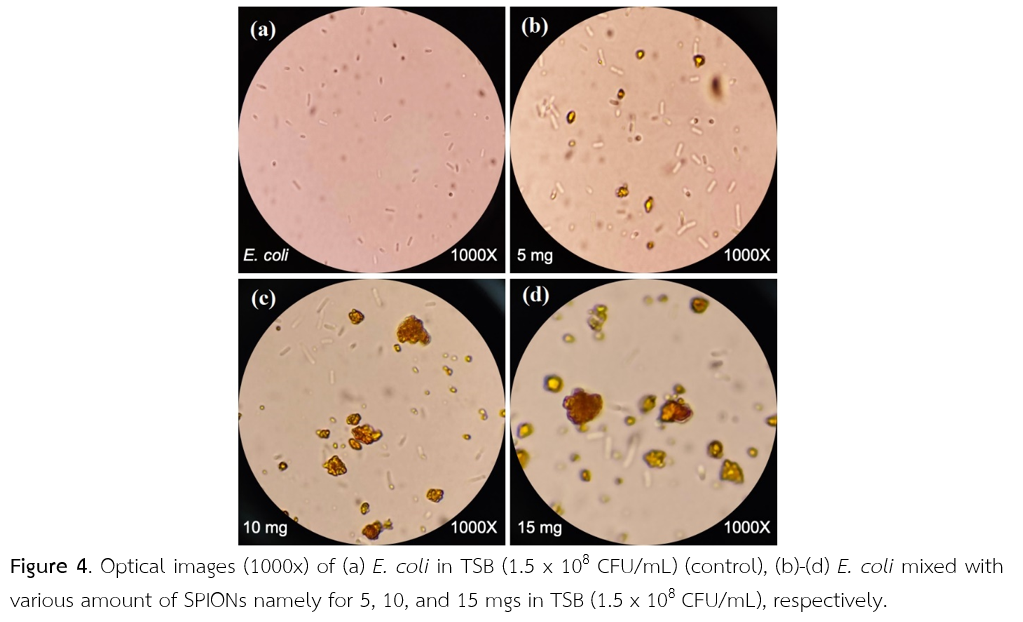
ความก้าวหน้าล่าสุดของการตรวจวัดสนามแม่เหล็กขนาดเล็กมากในระดับพิโคเทสลาภายใต้อุณหภูมิห้องโดยไม่มีการกำบังสนามแม่เหล็กภายนอกแสดงให้เห็นถึงศักยภาพในการนำวิธีดังกล่าวมาประยุกต์ใช้กับการทำเครื่องหมาย การติดฉลาก และการตรวจวัดทางแม่เหล็กของเป้าหมายเอกลักษณ์ทางชีวภาพ เช่น ไวรัส ยีนส์ โปรตีน และแบคทีเรีย ในบทความนี้ผู้วิจัยนำเสนอการตรวจวัดสนามแม่เหล็กของอนุภาคนาโนเหล็กออกไซด์ซุปเปอร์พาราแมกเนติกในอาหารเลี้ยงเชื้อแบบเหลว (Trypticase Soy Broth, TSB) และอนุภาคนาโนเหล็กออกไซด์ซุปเปอร์พาราแมกเนติกที่จับกับแบคทีเรียอีโคไล (E. coli) ในอาหารเหลว ซึ่งสนามแม่เหล็กของอนุภาคนาโนเหล็กออกไซด์ดังกล่าวที่จับกับแบคทีเรียอีโคไลถูกตรวจวัดได้ด้วยแมกเนติกด้วยแมกนีโตอิมพีแดนซ์เซ็นเซอร์ความไวสูง ค่าแรงดันไฟฟ้าที่วัดได้จากแมกนีโตอิมพีแดนซ์เซ็นเซอร์ของตัวอย่างที่มีแบคทีเรียอีโคไลมีค่าต่ำกว่าค่าแรงดันไฟฟ้าที่วัดได้จากตัวอย่างควบคุมอย่างมีนัยสำคัญ วิธีการทำให้ตัวอย่างเป็นเนื้อเดียวกันก่อนการวัดและการนำสนามแม่เหล็กภายนอกขนาดประมาณ 0.2 มิลลิเทสลาไปยังตัวอย่างทำให้เกิดการปรับแต่งสัญญาณที่วัดได้เด่นชัดขึ้น และได้มีการศึกษาเบื้องต้นของการตรวจวัดอนุภาคนาโนเหล็กนาโนเหล็กออกไซด์ซุปเปอร์พาราแมกเนติกที่จับกับเชื้ออีโคไลที่ปนเปื้อนในเครื่องดื่ม เทคนิคและการตรวจวัดอย่างง่ายสำหรับอนุภาคนาโนแม่เหล็กนี้สามารถนำไปสู่การพัฒนาต่อยอดเป็นไบโอเซนเซอร์ขนาดกระทัดรัดที่สามารถพกพาได้
Article Details

อนุญาตภายใต้เงื่อนไข Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
วารสารวิทยาศาสตร์และวิทยาศาสตร์ศึกษา (JSSE) เป็นผู้ถือลิสิทธิ์บทความทุกบทความที่เผยแพร่ใน JSSE นี้ ทั้งนี้ ผู้เขียนจะต้องส่งแบบโอนลิขสิทธิ์บทความฉบับที่มีรายมือชื่อของผู้เขียนหลักหรือผู้ที่ได้รับมอบอำนาจแทนผู้เขียนทุกนให้กับ JSSE ก่อนที่บทความจะมีการเผยแพร่ผ่านเว็บไซต์ของวารสาร
แบบโอนลิขสิทธิ์บทความ (Copyright Transfer Form)
ทางวารสาร JSSE ได้กำหนดให้มีการกรอกแบบโอนลิขสิทธิ์บทความให้ครบถ้วนและส่งมายังกองบรรณาธิการในข้อมูลเสริม (supplementary data) พร้อมกับนิพนธ์ต้นฉบับ (manuscript) ที่ส่งมาขอรับการตีพิมพ์ ทั้งนี้ ผู้เขียนหลัก (corresponding authors) หรือผู้รับมอบอำนาจ (ในฐานะตัวแทนของผู้เขียนทุกคน) สามารถดำเนินการโอนลิขสิทธิ์บทความแทนผู้เขียนทั้งหมดได้ ซึ่งสามารถอัพโหลดไฟล์บทความต้นฉบับ (Manuscript) และไฟล์แบบโอนลิขสิทธิ์บทความ (Copyright Transfer Form) ในเมนู “Upload Submission” ดังนี้
1. อัพโหลดไฟล์บทความต้นฉบับ (Manuscript) ในเมนูย่อย Article Component > Article Text
2. อัพโหลดไฟล์แบบโอนลิขสิทธิ์บทความ (Copyright Transfer Form) ในเมนูย่อย Article Component > Other
ดาวน์โหลด ไฟล์แบบโอนลิขสิทธิ์บทความ (Copyright Transfer Form)
เอกสารอ้างอิง
Anik, M. I., Hossain, M. K., Hossain, I., Mahfuz, A. M. U. B., Rahman, M. T. and Ahmed, I. (2021). Recent progress of magnetic nanoparticles in biomedical applications: A review. Nano Select, 2(6), 1146-1186. doi:10.1002/nano.202000162
Bonilla, M., Kolekar, S., Ma, Y., Diaz, H. C., Kalappattil, V., Das, R., Eggers, T., Gutierrez R.G., Phan, M.-H. and Batzill, M. (2018). Strong room-temperature ferromagnetism in VSe2 monolayers on van der Waals substrates. Nature Nanotechnology, 13(4), 289-293. doi:10.1038/s41565-018-0063-9
Devkota, J., Ruiz, A., Mukherjee, P., Srikanth, H. and Phan, M.-H. (2013a). Magneto-Impedance Biosensor With Enhanced Sensitivity for Highly Sensitive Detection of Nanomag-D Beads. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 49(7), 4060-4063. doi:10.1109/tmag.2012.2235414
Devkota, J., Wang, C., Ruiz, A., Mohapatra, S., Mukherjee, P., Srikanth, H. and Phan, M. H. (2013b). Detection of low-concentration superparamagnetic nanoparticles using an integrated radio frequency magnetic biosensor. Journal of Applied Physics, 113(10), 104701. doi:10.1063/1.4795134
Krishnan, K. M. (2017). Fundamentals and Applications of Magnetic Materials. New York: Oxford University Press.
Li, Z., Ma, J., Ruan, J. and Zhuang, X. (2019). Using Positively Charged Magnetic Nanoparticles to Capture Bacteria at Ultralow Concentration. Nanoscale Research Letters, 14(1), 195. doi:10.1186/s11671-019-3005-z
Liu, J., Su, D., Wu, K. and Wang, J.-P. (2020). High-moment magnetic nanoparticles. Journal of Nanoparticle Research, 22(3). doi:10.1007/s11051-020-4758-0
Makarov, D., Melzer, M., Karnaushenko, D. and Schmidt, O. G. (2016). Shapeable magnetoelectronics. Applied Physics Reviews, 3(1), 011101. doi:10.1063/1.4938497
Moghanizadeh, A., Ashrafizadeh, F., Varshosaz, J. and Ferreira, A. (2021). Study the effect of static magnetic field intensity on drug delivery by magnetic nanoparticles. Scientific Reports, 11(1), 18056. doi:10.1038/s41598-021-97499-7
Mohri, K., Humphrey, F. B., Panina, L. V., Honkura, Y., Yamasaki, J., Uchiyama, T. and Hirami, M. (2009). Advances of amorphous wire magnetics over 27 years. physica status solidi (a), 206(4), 601-607. doi:10.1002/pssa.200881252
Nakayama, S. and Uchiyama, T. (2015). Real-time measurement of biomagnetic vector fields in functional syncytium using amorphous metal. Scientific Reports, 5, 8837. doi:10.1038/srep08837
Quintana-Sánchez, S., Barrios-Gumiel, A., Sánchez-Nieves, J., Copa-Patiño, J. L., de la Mata, F. J. and Gómez, R. (2021). Bacteria capture with magnetic nanoparticles modified with cationic carbosilane dendritic systems. Materials Science and Engineering: C, 112622. doi:10.1016/j.msec.2021.112622
Sandhu A. and Handa H. (Ed.) (2018). Magnetic Nanoparticles for Medical Diagnostics. Bristal: IOP Publishing.
Sroysee, W., Ponlakhet, K., Chairam, S., Jarujamrus, P. and Amatatongchai, M. (2016). A sensitive and selective on-line amperometric sulfite biosensor using sulfite oxidase immobilized on a magnetite-gold-folate nanocomposite modified carbon-paste electrode. Talanta, 156-157, 154-162. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2016.04.066
Steel, A. (March, 14, 2022). Ultra-sensitive magnetic sensor. Retrieved from https://www.aichi-steel.co.jp/ENGLISH/smart/mi/products/type-dh.html
Uchiyama, T., Nakayama, S., Mohri, K. and Bushida, K. (2009). Biomagnetic field detection using very high sensitivity magnetoimpedance sensors for medical applications. physica status solidi (a), 206(4), 639-643. doi:10.1002/pssa.200881251
Wang, T., Zhou, Y., Lei, C., Luo, J., Xie, S. and Pu, H. (2017). Magnetic impedance biosensor: A review. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 90, 418-435. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2016.10.031
Wu, W., Wu, Z., Yu, T., Jiang, C. and Kim, W. S. (2015). Recent progress on magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: synthesis, surface functional strategies and biomedical applications. Science and Technology of Advanced Materials, 16(2), 023501. doi:10.1088/1468-6996/16/2/023501
Yang, Z., Liu, Y., Lei, C., Sun, X.-c. and Zhou, Y. (2015). A flexible giant magnetoimpedance-based biosensor for the determination of the biomarker C-reactive protein. Microchimica Acta, 182(15-16), 2411-2417. doi:10.1007/s00604-015-1587-4
Yang, Z., Liu, Y., Lei, C., Sun, X.-c. and Zhou, Y. (2016). Ultrasensitive detection and quantification of E. coli O157:H7 using a giant magnetoimpedance sensor in an open-surface microfluidic cavity covered with an antibody-modified gold surface. Microchimica Acta, 183(6), 1831-1837. doi:10.1007/s00604-016-1818-3
Zhong, J., Rosch, E. L., Viereck, T., Schilling, M. and Ludwig, F. (2021). Toward Rapid and Sensitive Detection of SARS-CoV-2 with Functionalized Magnetic Nanoparticles. ACS Sensor, 6(3), 976-984. doi:10.1021/acssensors.0c02160