Rapid detection of pathogenic bacteria with Superparamagnetic Iron-oxide Nanoparticles (SPIONs) using highly sensitive Magneto-impedance Sensor: A Preliminary Study
Main Article Content
Abstract
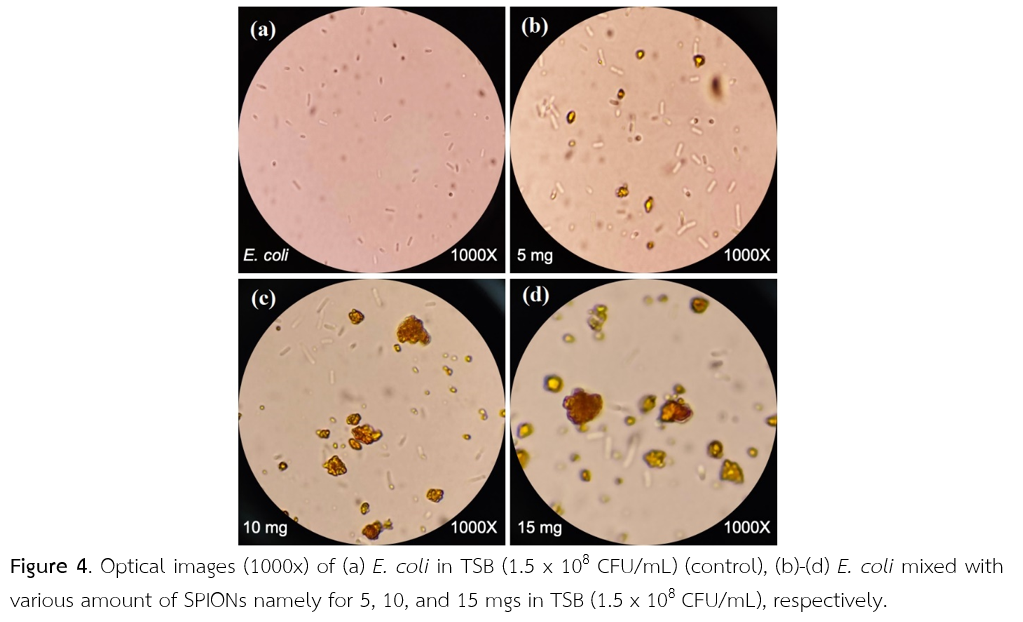
Recent progress in the detection of ultra-small magnetic fields down to nano-Tesla level at room temperature and without magnetic shielding has shown potential applications in magnetic marking, labeling, and detecting for target biological entities such as viruses, genes, proteins, and bacteria. Herein, we present the detection of stray magnetic fields of superparamagnetic iron-oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs) in liquid medium (Trypticase Soy broth, TSB) and SPIONs bound to test bacteria (Escherichia coli). The stray magnetic fields of SPIONs captured E. coli, and that of the control samples were measured using a highly sensitive magneto-impedance (MI) sensor. The output voltage of MI-sensor of SPIONs-captured E. coli sample was significantly lower than the control samples. Homogenizing samples prior detection and the introduction of the external static magnetic field, Hext, of ~ 0.2 mT to the samples showed remarkable enhancement of magnetic signals. The preliminary study of SPIONs capturedE. coli in dairy beverages has been performed. This simple and versatile technique for detecting magnetic nanoparticles can be further developed for a portable magnetic biosensor.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
The Journal of Science and Science Education (JSSE) retain the right of all articles published in JSSE. The coresponding author or the authorized person on behalf of the authors must send the complete Copyright Transfer Form to JSSE before any article get published in JSSE.
Copyright Transfer Form
The JSSE request the coresponding author or the authorized person on behalf of the authors upload the manuscript under the together with the Copyright Transfer Form under the supplementary data. The guidline for uploading both manuscript and Copyright Transfer Form is shown below:
1. Upload the manuscript in the sub-menu, Article Component > Article Text.
2. Upload the the Copyright Transfer Form in the sub-menu, Article Component > Other.
Download Copyright Transfer Form
References
Anik, M. I., Hossain, M. K., Hossain, I., Mahfuz, A. M. U. B., Rahman, M. T. and Ahmed, I. (2021). Recent progress of magnetic nanoparticles in biomedical applications: A review. Nano Select, 2(6), 1146-1186. doi:10.1002/nano.202000162
Bonilla, M., Kolekar, S., Ma, Y., Diaz, H. C., Kalappattil, V., Das, R., Eggers, T., Gutierrez R.G., Phan, M.-H. and Batzill, M. (2018). Strong room-temperature ferromagnetism in VSe2 monolayers on van der Waals substrates. Nature Nanotechnology, 13(4), 289-293. doi:10.1038/s41565-018-0063-9
Devkota, J., Ruiz, A., Mukherjee, P., Srikanth, H. and Phan, M.-H. (2013a). Magneto-Impedance Biosensor With Enhanced Sensitivity for Highly Sensitive Detection of Nanomag-D Beads. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 49(7), 4060-4063. doi:10.1109/tmag.2012.2235414
Devkota, J., Wang, C., Ruiz, A., Mohapatra, S., Mukherjee, P., Srikanth, H. and Phan, M. H. (2013b). Detection of low-concentration superparamagnetic nanoparticles using an integrated radio frequency magnetic biosensor. Journal of Applied Physics, 113(10), 104701. doi:10.1063/1.4795134
Krishnan, K. M. (2017). Fundamentals and Applications of Magnetic Materials. New York: Oxford University Press.
Li, Z., Ma, J., Ruan, J. and Zhuang, X. (2019). Using Positively Charged Magnetic Nanoparticles to Capture Bacteria at Ultralow Concentration. Nanoscale Research Letters, 14(1), 195. doi:10.1186/s11671-019-3005-z
Liu, J., Su, D., Wu, K. and Wang, J.-P. (2020). High-moment magnetic nanoparticles. Journal of Nanoparticle Research, 22(3). doi:10.1007/s11051-020-4758-0
Makarov, D., Melzer, M., Karnaushenko, D. and Schmidt, O. G. (2016). Shapeable magnetoelectronics. Applied Physics Reviews, 3(1), 011101. doi:10.1063/1.4938497
Moghanizadeh, A., Ashrafizadeh, F., Varshosaz, J. and Ferreira, A. (2021). Study the effect of static magnetic field intensity on drug delivery by magnetic nanoparticles. Scientific Reports, 11(1), 18056. doi:10.1038/s41598-021-97499-7
Mohri, K., Humphrey, F. B., Panina, L. V., Honkura, Y., Yamasaki, J., Uchiyama, T. and Hirami, M. (2009). Advances of amorphous wire magnetics over 27 years. physica status solidi (a), 206(4), 601-607. doi:10.1002/pssa.200881252
Nakayama, S. and Uchiyama, T. (2015). Real-time measurement of biomagnetic vector fields in functional syncytium using amorphous metal. Scientific Reports, 5, 8837. doi:10.1038/srep08837
Quintana-Sánchez, S., Barrios-Gumiel, A., Sánchez-Nieves, J., Copa-Patiño, J. L., de la Mata, F. J. and Gómez, R. (2021). Bacteria capture with magnetic nanoparticles modified with cationic carbosilane dendritic systems. Materials Science and Engineering: C, 112622. doi:10.1016/j.msec.2021.112622
Sandhu A. and Handa H. (Ed.) (2018). Magnetic Nanoparticles for Medical Diagnostics. Bristal: IOP Publishing.
Sroysee, W., Ponlakhet, K., Chairam, S., Jarujamrus, P. and Amatatongchai, M. (2016). A sensitive and selective on-line amperometric sulfite biosensor using sulfite oxidase immobilized on a magnetite-gold-folate nanocomposite modified carbon-paste electrode. Talanta, 156-157, 154-162. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2016.04.066
Steel, A. (March, 14, 2022). Ultra-sensitive magnetic sensor. Retrieved from https://www.aichi-steel.co.jp/ENGLISH/smart/mi/products/type-dh.html
Uchiyama, T., Nakayama, S., Mohri, K. and Bushida, K. (2009). Biomagnetic field detection using very high sensitivity magnetoimpedance sensors for medical applications. physica status solidi (a), 206(4), 639-643. doi:10.1002/pssa.200881251
Wang, T., Zhou, Y., Lei, C., Luo, J., Xie, S. and Pu, H. (2017). Magnetic impedance biosensor: A review. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 90, 418-435. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2016.10.031
Wu, W., Wu, Z., Yu, T., Jiang, C. and Kim, W. S. (2015). Recent progress on magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: synthesis, surface functional strategies and biomedical applications. Science and Technology of Advanced Materials, 16(2), 023501. doi:10.1088/1468-6996/16/2/023501
Yang, Z., Liu, Y., Lei, C., Sun, X.-c. and Zhou, Y. (2015). A flexible giant magnetoimpedance-based biosensor for the determination of the biomarker C-reactive protein. Microchimica Acta, 182(15-16), 2411-2417. doi:10.1007/s00604-015-1587-4
Yang, Z., Liu, Y., Lei, C., Sun, X.-c. and Zhou, Y. (2016). Ultrasensitive detection and quantification of E. coli O157:H7 using a giant magnetoimpedance sensor in an open-surface microfluidic cavity covered with an antibody-modified gold surface. Microchimica Acta, 183(6), 1831-1837. doi:10.1007/s00604-016-1818-3
Zhong, J., Rosch, E. L., Viereck, T., Schilling, M. and Ludwig, F. (2021). Toward Rapid and Sensitive Detection of SARS-CoV-2 with Functionalized Magnetic Nanoparticles. ACS Sensor, 6(3), 976-984. doi:10.1021/acssensors.0c02160