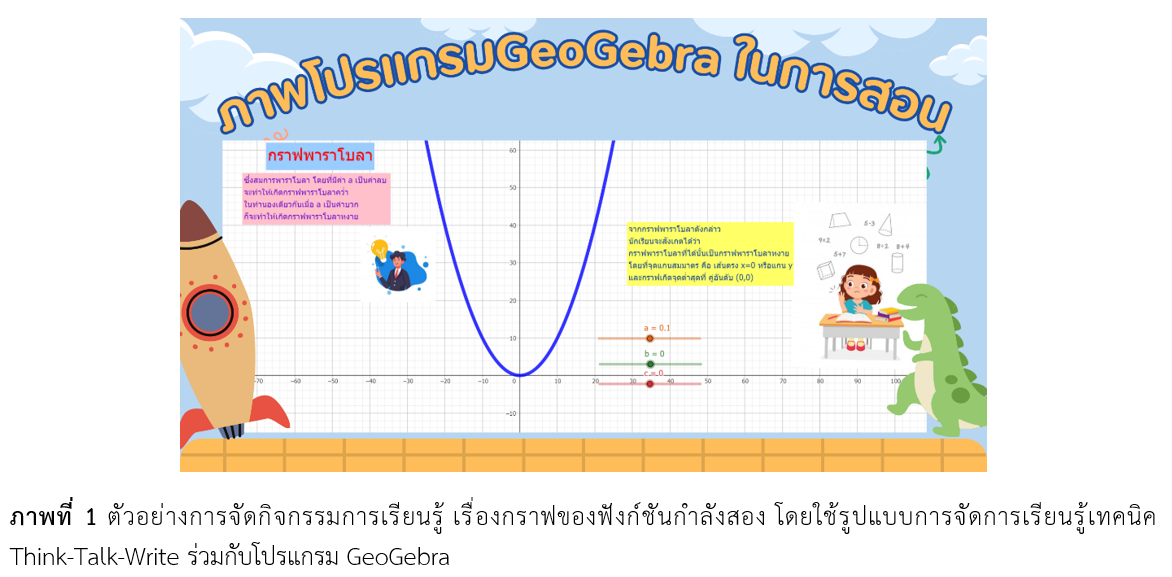
การพัฒนาความยึดมั่นผูกพันในการเรียนซึ่งมีผลต่อผลสัมฤทธิ์ทางการเรียนวิชาคณิตศาสตร์เรื่องกราฟของฟังก์ชันกำลังสองของนักเรียนชั้นมัธยมศึกษาปีที่ 3 โดยใช้การจัดการเรียนรู้เทคนิค Think-Talk-Write ร่วมกับโปรแกรม GeoGebra
Main Article Content
บทคัดย่อ
การวิจัยครั้งนี้มีวัตถุประสงค์เพื่อ 1) เปรียบเทียบความยึดมั่นผูกพันในการเรียนวิชาคณิตศาสตร์ เรื่องกราฟของฟังก์ชันกำลังสองของนักเรียนชั้นมัธยมศึกษาปีที่ 3 และ 2) เปรียบเทียบผลสัมฤทธิ์ทางการเรียนวิซาคณิตศาสตร์ เรื่องกราฟของฟังก์ชันกำลังสองของนักเรียนชั้นมัธยมศึกษาปีที่ 3 ก่อนและหลังการจัดการเรียนรู้ด้วยเทคนิค Think-Talk-Wite ร่วมกับ โปรแกรม GeoGebra กลุ่มตัวอย่างที่ใช้ในการวิจัย ได้แก่ นักเรียนชั้นมัยมศึกษาปีที่ 3 โรงเรียนแห่งหนึ่งในจังหวัดกาฬสินธุ์ ภาคเรียนที่ 1 ปีการศึกษา 2566 จำนวน 43 คน โดยการสุ่มตัวอย่างแบบง่าย เครื่องมือในการวิจัย ได้แก่ แผนการจัดการเรียนรู้ แบบทดสอบวัดผลสัมฤทธิ์ทางการเรียน และแบบวัดความยึดมั่นผูกพันในการเรียน สถิติที่ใช้ในการวิเคราะห์ข้อมูล ได้แก่ ค่าเฉลี่ย ส่วนเบี่ยงเบนมาตรฐาน ร้อยละ และการทดสอบค่าทีแบบตัวอย่างไม่เป็นอิสระต่อกัน โดยการจัดการเรียนรู้ด้วยเทคนิค ThinkTalk-Wite ร่วมกับ โปรแกรม GeoGebra ผลการวิจัยพบว่า 1) ผลความยึดมั่นผูกพันในการเรียนวิชาคณิตศาสตร์เรื่องกราฟของฟังก์ชันกำลังสองของนักเรียนชั้นมัธยมศึกษาปีที่ 3 หลังเรียนสูงกว่าก่อนเรียน อย่างมีสถิติที่ระดับ .05 2) ผลสัมฤทธิ์ทางการเรียนวิชาคณิตศาสตร์ เรื่องกราฟของฟังก์ชันกำลังสอง ของนักเรียนขั้นมัธยมศึกษาปีที่ 3 หลังเรียนสูงกว่าก่อนเรียน อย่างมีนัยสำคัญทางสถิติที่ระดับ .05
Article Details

อนุญาตภายใต้เงื่อนไข Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
วารสารวิทยาศาสตร์และวิทยาศาสตร์ศึกษา (JSSE) เป็นผู้ถือลิสิทธิ์บทความทุกบทความที่เผยแพร่ใน JSSE นี้ ทั้งนี้ ผู้เขียนจะต้องส่งแบบโอนลิขสิทธิ์บทความฉบับที่มีรายมือชื่อของผู้เขียนหลักหรือผู้ที่ได้รับมอบอำนาจแทนผู้เขียนทุกนให้กับ JSSE ก่อนที่บทความจะมีการเผยแพร่ผ่านเว็บไซต์ของวารสาร
แบบโอนลิขสิทธิ์บทความ (Copyright Transfer Form)
ทางวารสาร JSSE ได้กำหนดให้มีการกรอกแบบโอนลิขสิทธิ์บทความให้ครบถ้วนและส่งมายังกองบรรณาธิการในข้อมูลเสริม (supplementary data) พร้อมกับนิพนธ์ต้นฉบับ (manuscript) ที่ส่งมาขอรับการตีพิมพ์ ทั้งนี้ ผู้เขียนหลัก (corresponding authors) หรือผู้รับมอบอำนาจ (ในฐานะตัวแทนของผู้เขียนทุกคน) สามารถดำเนินการโอนลิขสิทธิ์บทความแทนผู้เขียนทั้งหมดได้ ซึ่งสามารถอัพโหลดไฟล์บทความต้นฉบับ (Manuscript) และไฟล์แบบโอนลิขสิทธิ์บทความ (Copyright Transfer Form) ในเมนู “Upload Submission” ดังนี้
1. อัพโหลดไฟล์บทความต้นฉบับ (Manuscript) ในเมนูย่อย Article Component > Article Text
2. อัพโหลดไฟล์แบบโอนลิขสิทธิ์บทความ (Copyright Transfer Form) ในเมนูย่อย Article Component > Other
ดาวน์โหลด ไฟล์แบบโอนลิขสิทธิ์บทความ (Copyright Transfer Form)
เอกสารอ้างอิง
Dila, D. O. (2012). Think-Talk-Write strategies. Retrieved 23 December 2023, from dila’ s story: http://syahputri90dila.blogspot.com/2012/01/metode-pembelajaran-bahasainggris_12.html
Fonglam. P. (2011). Problems in organizing the teaching and learning of general mathematics courses. (in Thai) Master's Thesis. Bangkok: Sripatum University.
Fredricks, J. A., Blumenfeld, P. C. and Paris, A. H. (2004). School engagement: Potential of the concept, state of the evidence. Review of educational research, 74 (1), 59-109.
Gafoor, K. A. and Kurukkan, A. (2015). Why High School Students Feel Mathematics Difficult? An Exploration of Affective Beliefs. Pedagogy of Teacher Education: Trends and Challenges, 23-27. 147887365.
Hurst, S. (2013). Seven ways to increase student engagement in the classroom. Retrieved 23 December 2023, Reading Horizons: https://readinghorizons.website/blog/seven-ways-to-increase-student-engagement-in-the-classroom/
Kruedsanoi. P. and Kaewpuang, P. (2023). Development of educational game activity packages for enhancing learning engagement and learning achievement in economics for seventh grade students (in Thai). Journal of MCU Social Science Review, 12(3), 150–165.
Ministry of Education. (2017). Learning standards and indicators. Mathematics learning group (revised edition 2017) according to the Basic Education Core Curriculum 2008 (in Thai). Bangkok: Agricultural Cooperative Assembly Printing Press Thailand Co., Ltd.
Pasong, A. (2016). Using the GeoGebra program to support 4MAT learning to develop academic achievement. study mathematics about basic calculus for grade 12 students (in Thai). Master's Thesis. Nakhon Ratchasima: Nakhon Ratchasima Rajabhat University.
Phattharakorn, S. (2009). The effect of organizing active learning on problem solving and mathematical communication abilities of Mathayomsuksa III students in probability (in Thai). Master's Thesis. Bangkok: Srinakharinwirot University.
Piper, L., Marchand-Martella, N. and Martella, R. (2010). Use of explicit instruction and double-dosing to teach ratios, proportions, and percentages to at-risk middle school students. The Journal of At-Risk Issues, 15(2), 9-17.
Suwannatthachot. P. (2018). Active Learning (in Thai). Bangkok: Chulalongkorn University Printing House.
The Institute for the Promotion of Teaching Science and Technology (IPST). (2017). Report on research results of the TIMSS 2015 project (in Thai). Retrieved 23 December 2023, from https ://timssthailand.ipst.ac.th/timss/reports/timss2015report
The Institute for the Promotion of Teaching Science and Technology (IPST). (2017). Mathematics learning group course manual. (Revised edition 2017) Lower secondary school level (in Thai). Retrieved 23 December 2023, from SciMath knowledge base: https://www.scimath.org/ebook-mathematics/item/8380-2560-2551-8380
Thipraksa. W. (2017). A study of understanding and learning retention on parabola for grade 9 students by using learning activities through GeoGebra (in Thai). Master's Thesis. Ubon Ratchathani: Ubon Ratchathani. University.
Thongnak. P. (2016). The effects of organizing learning activities through heuristics with Think-Talk-Write technique on mathematical problem solving and communication abilities of Mathayomsuksa four students (in Thai). Journal of Education, 29(1), 127-142.
Wang, M. T. and Holcombe, R. (2010). Adolescents’ perceptions of school environment, engagement, and academic achievement in middle school. American educational research journal, 47(3), 633-662.
Willms, J. D. (2003). Student engagement at school: A sense of belonging and participation: Results from PISA 2000. Retrieved 23 December 2023, from OECD iLibrary: https://www.oecd-ilibrary.org/education/student-engagement-at-school_9789264018938-en?fbclid=IwAR3B99LbTvXF04MVpj-_3ZqGdrE3ojnl5Qisy0eDqbTCTktouq324UJ7ZWw
Wuttisant. P. (2023). GeoGebra, another interesting option for mathematics teachers (in Thai). Retrieved 23 December 2023, from SciMath knowledge base system: https://www.scimath.org/article-mathematics/item/12824-geogebra