THE INFLUENCING OF CAUSAL FACTORS TO THE LOYALTY OF COMMERCIAL BANKS' CUSTOMERS IN SAKON NAKHON MUNICIPALITY, SAKON NAKHON PROVINCE
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.14456/nrru-rdi.2020.46Keywords:
Customer loyalty, Commercial bankAbstract
The purposes of this study is to study the causal factors influencing the loyalty of commercial banks' customers in Sakon Nakhon municipality, Sakon Nakhon and to examine the partial least square structural equation that loyalty of commercial models banks' customers in Sakon Nakhon municipality. Taro Yamane formula was used to find the sample size with an unknown population of 385 samples, reserve a loss of 15 samples total of 400 samples. The sampling group was classified by consumers in commercial banks. The questionnaire was used as the data collection instrument. The statistical analysis used for analysis consisted of percentage and Partial Least Square Structural Equation Modelling (PLS-SEM).
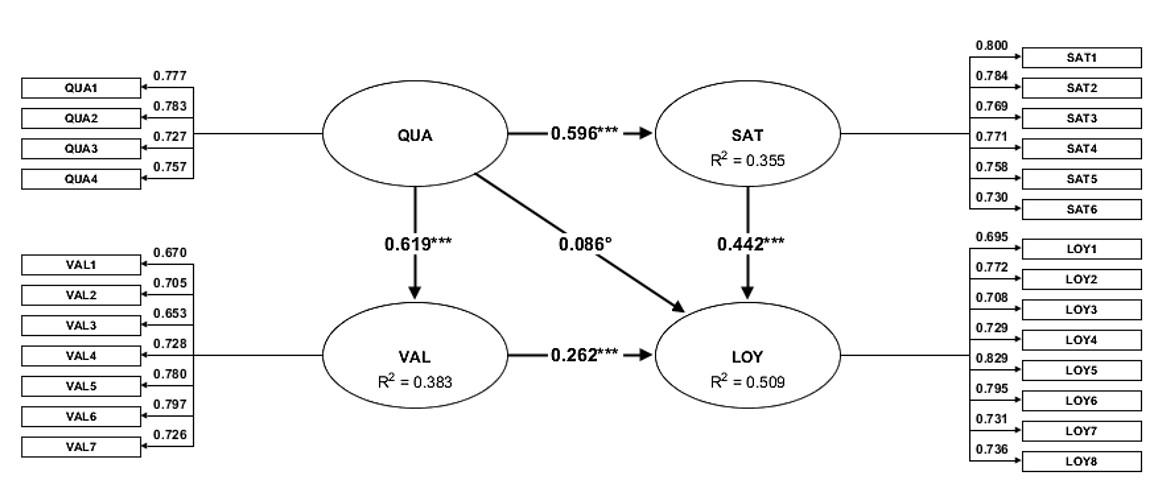
The results indicate that perceived service quality has a significantly positive effect on perceived value (b=0.6187, p<0.000), has a significantly positive effect on customer satisfaction (b=0.5960, p<0.000) but has not a significantly positive effect on customer loyalty (b=0.0859, p<0.060). Perceived Value has a significantly positive effect on customer loyalty (b=0.2624, p<0.000) and customer satisfaction has a significantly positive effect on customer loyalty (b=0.4421, p<0.000). For the result of examine the partial least square structural equation that loyalty of commercial models banks' customers in Sakon Nakhon municipality. The results reveal the reliability and validity of the Measurement Model (Outer) and Construct Model (Inner) path model.
References
AL-HAWARY, S. I., & Hussien, A. J. (2016). The Impact of electronic banking services on the Customers Loyalty of Commercial Banks in Jordan. International Journal of Academic Research in Accounting, Finance and Management Sciences, 7(1), 50-63.
Ashraf, S., Ilyas, R., Imtiaz, M., & Ahmad, S. (2018). Impact of service quality, corporate image and perceived value on brand loyalty with presence and absence of customer satisfaction: A study of four service sectors of Pakistan. International Journal of Academic Research in Business and Social Sciences, 8(2), 452-474.
Bagozzi, R. P. ,& Yi, Y. (1988). On the evaluation of structural equation model. Journal of Academy of Marketing Science, 16(1), 74-94.
Bitner, M. J., & Hubbert, A. R. (1994). Encounter satisfaction versus overall satisfaction versus quality: The customer’s voice. In Rust, R.T., & Oliver, R.L. (Eds.). Service quality : New directions in theory and practice. Thousand Oaks, CA : Sage.
Chin, W. W. (1998) The partial least squares approach to structural equation modeling. Modern Methods For Business Research, 295, 295-336.
Cohen, S. (2013). States of denial: Knowing about atrocities and suffering: John Wiley & Sons.
Culiberg, B. & Rojšek, I. (2010). Identifying service quality dimensions as antecedents to customer satisfaction in retail banking. Economic and Business Review, 12(3), 151-166.
Dijkstra, T. K., & Henseler, J. (2015). Consistent partial least squares path modeling. MIS Quarterly = Management Information Systems Quarterly, 39(2), 297-316.
Felix, R. (2017). Service quality and customer satisfaction in selected banks in Rwanda. Journal of Business & Financial Affairs, 6(1), 1-11.
Fornell, C., & Larcker, D. F. (1981). Evaluating structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error. Journal of Marketing Research, 18(1), 39-50.
Geok Theng Lau. (1999). Consumer’s Trust in a brand and the link to brand loyalty. Singapore: Public of Singapore, 4(4), 341-370.
Hair, J. F., Black, W. C., Babin, B. J., & Anderson, R. E. (2010). Multivariate data analysis (7th ed.). Upper Saddle River, NJ : Prentice Hall.
Hair, J. F., Ringle, C. M., & Sarstedt, M. (2013). Partial least squares structural equation modeling: Rigorous applications, better results and higher acceptance. Long Range Planning, 46(1-2), 1-12.
Henseler, J., Hubona, G., & Ray, P. A. (2016). Using PLS path modeling in new technology research: Updated guidelines. Industrial Management & Data Systems, 116(1), 2-20.
Henseler, J., Ringle, C. M., & Sarstedt, M. (2015). A new criterion for assessing discriminantvalidity in variance-based structural equation modeling. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 43(1), 115-135.
Hulland, J. (1999). Use of partial least squares (PLS) in strategic management research: A review of four recent studies. Strategic Management Journal, 20, 195-224.
Jhantasana, C. (2018). The path analysis of islander’benefit to support for tourism development using pls-sem, Nida Business Journal Volume, 20(1), 54-89. (In Thai)
Kant, R., & Jaiswal, D. (2017). The impact of perceived service quality dimensions on customer satisfaction: An empirical study on public sector banks in India, International Journal of Bank Marketing, 35(3), 411-430.
Kongprepan, H. (2014). Effects of service quality on customer loyalty: A comparison between Krung Thai Bank (PCL) and Bangkok Bank (PCL) in Amphoe Muang, Pathumthani province, Independent study according, Bachelor of Business Administration Degree Program in Faculty of Business Administration, Rajamangala University of Technology Thanyaburi, Pathumthani. (In Thai)
Makanyeza, C., & Chikazhe, L. (2017). Mediators of the relationship between service quality and customer loyalty. International Journal of Bank Marketing, 35(3), 540-556.
Malisorn, P., & Techamaneesatit, T. (2014). Customer Service that Effect Customer Loyalty of Supercenter. National Research Conference 2014, pp. 446-474.
Monchantha, S., & WiraPhaibun, W. (2018). A Causal Relationship Model of the Influences of Service Quality on Customer Satisfaction, Trust, and Loyalty of KTB, Kanchanaburi Branch, Veridian E-Journal,Silpakorn University (Humanities, Social Sciences and arts) Current, 11(2), 2982-2996. (In Thai)
Nunnally, J. C. (1967), Psychometric theory (1st ed.). New York : McGraw-Hill.
Parasuraman, A., Zeithaml, V. A., & Berry, L. L. (1985). A conceptual model of service quality and its implications for future research. Journal of Marketing (Fall), 41-50.
Positioning. (2015). Projections for thai bank results. Retrieved January 25, 2020, form https:// positioningmag.com/28403 (In Thai)
Rovinelli, R. J., & Hambleton, R. K. (1977). On the use of content specialists in the assessment of criterion-referenced test item validity. Dutch Journal of Educational Research, 2, 49-60.
Ruankaew, J. (2007). Factors affecting the selection Service from commercial banks Of students in social sciences at the bachelor degree level Chiang Mai University. Independent Study, Master of Economics Program degree in Faculty of Economics, Chiang Mai University, Chiang Mai. (In Thai)
Stone, M. (1974). Cross-validation choice and assessment of statistical predictions. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, 36, 111-133.
Vanichbancha, K. (2010). Advanced statistical analysis with SPSS for Windows (8th ed.). Bangkok : Thammasarn. (In Thai)
Yamane, T. (1973 ). Statistics: An introductory analysis (3rd Ed.). New York : Harper and Row Publications.
Zahir O., Liana M., & Ratna K. M. (2015). An empirical study of direct relationship of service quality, customer satisfaction and bank image on customer loyalty in Malaysian commercial banking industry. American Journal of Economics, 5(2), 168-176.