DEVELOPMENT OF A BLENDED LEARNING MODEL BY USING AN ACTIVE LEARNING METHOD TO ENHANCE PRE-SERVICE TEACHER EDUCATION STUDENTS’ INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY (ICT) COMPETENCIES
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.14456/nrru-rdi.2021.36Keywords:
Model of blended learning, Active learning method, ICT competencies, Pre-service teacher education studentsAbstract
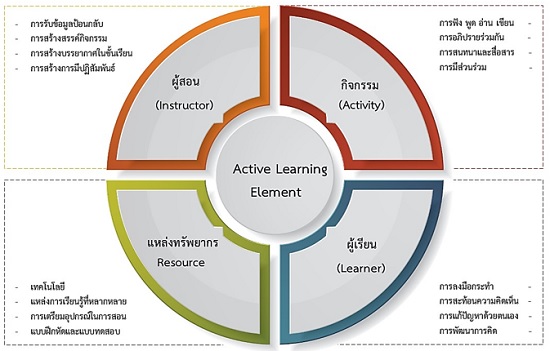
The two purposes of this research were: 1) to analyze and synthesize a blended learning model by using an active learning method designed to enhance pre-service teacher education students’ ICT competencies; and 2) to develop a blended learning model by using an active learning method to enhance pre-service teacher education students’ ICT competencies. The study’s procedure was divided into 2 steps: 1) synthesizing the models through the technique of document synthesis. The sample selected by purposive sampling was experts in education, totaling 5 people. An interview guide was used to collect data which then were synthesized for the development of the instructional model; and 2) assessing the appropriateness of the instructional model. The sample was 5 experts for assessing the appropriateness of the instructional model. A 5-point rating scale questionnaire was used to collect data. Data analysis was conducted using mean and standard deviation. The three main findings of the research were as follows: The model was composed of 4 elements: 1) instructor, 2) learner, 3) classroom, 4) technology and the model of blended learning by using an active learning method was appropriately suitable at the highest level ( =4.91, S.D.=0.15); and 3) the model of blended learning by using an active learning method achieved a quality at the highest level ( =4.92, S.D.=0.11).
References
Allen, I. E., & Seaman, J. (2010). Blended Learning. Retrieved March 8, 2018, from https://goo.gl/DRmsJ1
Bonwell, C. C. (2003). Active Learning: Creating Excitement in the Classroom. Retrieved May 14, 2019, from shorturl.at/fGJVY
Bonwell, C. C., & Eison, J. A. (1991). Active learning: Creating excitement in the classroom. Retrieved May 14, 2019, from shorturl.at/clmnG
Boonprakob, M. (2000). Research and Development of Science-Based Teaching Techniques Guidelines for Raising the Quality of Science Education. Bangkok: Institute for the Promotion of Teaching Science and Technology.
Carman, J. M. (2005). Blended Learning Design: FiveKey Ingredients. Retrieved May 14, 2019, from https://goo.gl/Eoyztf
Cronbach, L. J. (1970). Other characteristics desired in tests. Essentials of Psychological Testing, 160-161.
Ditsiri, T. (2017). The Study of Teachers’ of Information and Communication Technology Competencies for the 21st Century in Students of Educational Technology and Computer at Faculty of Education Chandrakasem Rajabhat University. Retrieved August 27, 2020, from shorturl.at/eGJM6
Ditsiri, T. (2018). The Study Needs of Students in Educational Technology and Computers at Faculty of Education Chandrakasem Rajabhat University for Blended Learning in Offline Learning and Online Learning. Retrieved August 27, 2020, from shorturl.at/nuGP7
Driscoll, M. (2002). Blended Learning: Let's get beyondthe hype. Learning and Training Innovations Newsline. Retrieved May 14, 2019, from https://goo.gl/EK14SB
Fesol, S. F. A., & Salam, S. (2016). Towards MOOC for technical courses: A blended learning empirical analysis. In 2016 4th International Conference on User Science and Engineering (i-USEr) (pp. 116-121). IEEE.
Graham, C. R. (2005). Blended learning systems: Definition, current trends, and future directions. San Francisco : Pfeiffer Publishing.
Graham, C. R. (2012). Blended Learning. Retrieved May 14, 2019, from https://goo.gl/DRmsJ1
Harkins, A. M. (2017). Leapfrog Principlep and Practicep : Core Components of Education 3.0 and 4.0. Retrieved May 14, 2019, from shorturl.at/yCG38
Kabilan, M. K. (2004). Online Professional Development : A Literature Analysis of Teacher Competency. Journal of Computing in Teacher Education, 21(2), 51-57.
Kaewurai, R. (2007). Blended learning. Retrieved May 6, 2019, from shorturl.at/mryX8
Likert, R. A. (1961). New Patterns of Management. New York : McGraw-Hill Book.
Meyers, C., & Jones, T. B. (1993). Promoting Active Learning: Strategies for the College Classroom. San Francisco : Jossey-Bass Publishers.
Nilsook, P., & Wannapiroon, P. (2014). Blended Management Learning : Blended Ratio. Journal of Technical Education Development, 25(85), 31-36.
Office of Academic Affairs and Educational Standards. (2017). The guidelines for selecting a prototype school to reduce time additional learning time: Active Learning. Retrieved May 12, 2019, from shorturl.at/nCGU5
Office of Policy and Strategy, Office of the Permanent Secretary, Ministry of Education. (2016). Educational Development Plan of Ministry of Education, 12(2017-2021). Retrieved May 6, 2019, from shorturl.at/ktL57
Promphasit, P. (2016). Active Learning (AL) for HuSo at KPRU. Retrieved April 25, 2019, from shorturl.at/jzX01
Ruokonen, I. (2016). E-Learning in Music: A Case Study of Learning GroupComposing in a Blended Learning Environment. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, 21, 109-115.
Salemi, M. K. (2002). An Illustrated Case for Active Learning. Southern Ecomomic Journal, 68(3), 721-731.
Thorne, K. (2003). Blended learning: how to integrateonline and traditional learning. London : Kogan Page.