The Effects of Promoting an Early Childhood Teachers’ Competency Enhancement Program on Executive Function Skills of Young Children: A Study in the Integrated Area of Tha Muang District, Kanchanaburi Province
Main Article Content
Abstract
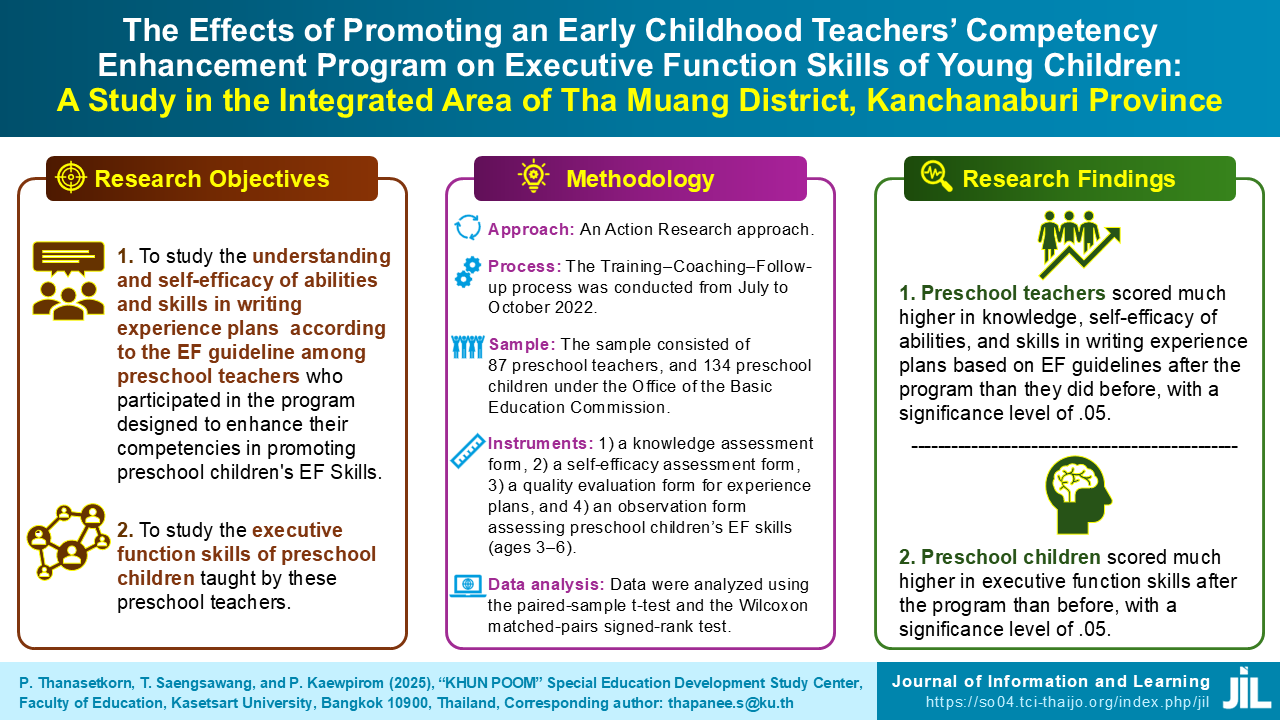
This research aims to 1) study the understanding and self-efficacy of abilities and skills in writing experience plans according to the EF guideline among preschool teachers who participated in the program designed to enhance their competencies in promoting preschool children's executive function skills; and 2) study the executive function skills of preschool children taught by these preschool teachers. The study adopted an action research approach based on Kemmis et al.'s (2014) principles. Tha Muang District in Kanchanaburi Province served as the research site. The sample group consisted of 87 preschool teachers from the Office of the Basic Education Commission and local administrative organizations, as well as 134 preschool children from the Office of the Basic Education Commission. The study was conducted from July to October 2022. The research tools comprised (1) a knowledge assessment form, (2) a self-efficacy assessment form, (3) a quality inspection form for experience plans, and (4) an observation form for preschool children's executive function skills (ages 3–6). Data were analyzed using the paired sample t-test and the Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed-rank test. The research findings showed that 1) preschool teachers scored much higher in knowledge, self-efficacy of abilities, and skills in writing experience plans based on EF guidelines after the program than they did before, with a significance level of .05, and 2) preschool children scored much higher in executive function skills after the program than before, with a significance level of .05. According to the findings, the program enhances instructors’ planning abilities and positively influences preschool children’s executive function skills.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
The Journal of Information and Learning is operated by the Office of Academic Resources, Prince of Songkla University. All articles published in the journal are protected by Thailand copyright law. This copyright covers the exclusive rights to share, reproduce and distribute the article, including in electronic forms, reprints, translations, photographic reproductions, or similar. Authors own copyrights in the works they have created as well as the Office of Academic Resources. The Journal reserves the right to edit the language of papers accepted for publication for clarity and correctness, as well as to make formal changes to ensure compliance with the journal's guidelines. All authors must take public responsibility for the content of their paper.
References
Chawaphanth, K., & Bangtit, P. (2024). Integrating executive functions into surveillance and promotion of early childhood development through the adult learning program. Journal of Nursing and Education, 17(2), 1–13. https://he01.tci-thaijo.org/index.php/JNAE/article/view/267449
Chutabhakdikul, N. (2018). Khumu phomæ phatthanā thaksa samōng EF–executive function tangtǣ patisonthi–sām pī [Parent's guide to developing EF–executive function from conception to 3 years]. Aksorn Sampan Press.
Domínguez-Salas, S., Díaz-Batanero, C., Lozano-Rojas, O. M., & Verdejo-García, A. (2016). Impact of general cognition and executive function deficits on addiction treatment outcomes: Systematic review and discussion of neurocognitive pathways. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 71, 772–801. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2016.09.030
Ferguson, H. J., Brunsdon, V. E. A., & Bradford, E. E. F. (2021). The developmental trajectories of executive function from adolescence to old age. Scientific Reports, 11, Article 1382. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-80866-1
Friedman, N. P., & Robbins, T. W. (2022). The role of prefrontal cortex in cognitive control and executive function. Neuropsychopharmacology, 47(1), 72–89. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41386-021-01132-0
Furr, R. M. (2008). Summary of effect sizes and their links to inferential statistics. Department of Psychology, Wake Forest University. https://furrrm.sites.wfu.edu/wp-content/uploads/2018/09/EffectSizeFormulas.pdf
Harnmethee, S., Pitaksinsuk, T., & A-ramrit, B. (2018). Khumu phatthanā thaksa samōng EF–executive function samrap khrū pathommawai [EF–executive function skills development guide for early childhood teachers]. Matichon.
Kemmis, S., McTaggart, R., & Nixon, R. (2014). The action research planner: Doing critical participatory action research. Springer.
Knowles, M. S., Holton, E. F., & Swanson, R. A. (2011). The adult learner: The definitive classic in adult education and human resource development (7th ed.). Elsevier.
Ministry of Education. (2017). Early childhood education curriculum 2017. Agricultural Cooperative Printing House of Thailand.
Ministry of Public Health. (2022). Developmental surveillance and promotion manual (DSPM). https://www.mhc2.go.th/ML/docs/doc_201630721820230209_230650.pdf
Ngernbamrung, A. (2023). Thalǣng khāo "wō̜n ratthabān mai rē ngō̜ sāng phūm tānthān tangtǣ pathommawai tœ̄ptō pai mai chai yāsēptit" [Press conference: "Ask the new government to build immunity from early childhood, so that when they grow up, they don't use drugs."]. Mahidol University. https://mahidol.ac.th/temp/2023/05/Press-cf.pdf
Office of the Prime Minister. (2016, December 29). Prakāt rư̄ang phāen phatthanā setthakit lae sangkhom hāeng chāt chabap thī sip song (B.E. 2560–2564) [Announcement on the 12th National Economic and Social Development Plan (2017 – 2021)]. Office of the National Economic and Social Development Council. https://www.nesdc.go.th/wp-content/themes/plant3-child/assets/pdf/12/article_20170202134836.pdf
Palitpholkarnpim, P. (2019). Sāng dek phūm dī dūai EF [Create healthy children with EF]. Amarin Printing & Publishing.
Pentz, M. A., Riggs, N. R., & Warren, C. M. (2016). Improving substance use prevention efforts with executive function training. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 163(1), S54–S59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2016.03.001
Perone, S., Simmering, V. R., & Buss, A. T. (2021). A dynamical reconceptualization of executive-function development. Perspectives on Psychological Science, 16(6), 1198–1208. https://doi.org/10.1177/1745691620966792
Phueakphet, N., Thanasetkorn, P., & Seree, P. (2022). The impact of learning-experience activities based on Trisikkha principle and EF guideline on preschoolers’ self-regulation skills. Ratchaphruek Journal, 20(3), 59–72. https://so05.tci-thaijo.org/index.php/Ratchaphruekjournal/article/view/259415
Podhayanukul, W., Thanasetkorn, P., Seree, P., & Jiawiwatkul, A. (2020). The impacts of the EF guideline program on executive function skills: A follow-up study of children in the classrooms where lesson plans were based on EF guideline in Bangkok. Journal of Education Research, 15(1), 27–44. https://ejournals.swu.ac.th/index.php/jre/article/view/12818
Poolbun, P. (2020). Development of a teacher professional development model to enhance the science teaching ability using scientific argumentation for pre-service science teachers [Doctoral dissertation, Srinakharinwirot University]. iThesis Srinakharinwirot University. https://ir-ithesis.swu.ac.th/items/70998f09-1e8b-48c1-b2b3-f184d2bda35d
Sukamolson, S. (2010). Effect size: Practical significance in research. Pasaa Paritat Journal, 25, 26–38. https://www.culi.chula.ac.th/Images/asset/pasaa_paritat_journal/file-25-148-dvkis2254169.pdf
Thanasetkorn, P. (2021). EF thaksa samōng phư̄a čhatkān chīwit hai samret læ yū rō̜t dai nai lōk thī prǣprūan (executive function) [EF: executive function to successfully manage life and survive in a VUCA world]. Aksorn Sampan Press.
Thanasetkorn, P., Suttipan, P., Tamaekong, A., Archan, C., Imtaku, P., Permsaphirun, S., Winyakul, P., Podhayanukul, W., & Mekboworn, M. (2018). EF guideline khrư̄angmư̄ wikhro phuea okbāep "Kān chat prasopkārn thī songsœm thaksa samong EF" samrap khrū pathomwai [EF guideline: An analysis tool for designing “experiences that promote executive function skills” for early childhood teachers]. Thai Health Promotion Foundation. https://www.thaihealth.or.th/wp-content/uploads/2020/02/616.pdf
Yoskhamlue, S. (2021). Developing the teacher’s learning management program using brain-based learning for schools under the Office of Udonthani Primary Educational Service Area 3 [Master’s thesis, Mahasarakham University]. Mahasarakham University Intellectual Repository. http://202.28.34.124/dspace/bitstream/123456789/1041/1/59030580048.pdf