The Production of Stop Cyberbullying Animation Media: Stop Cyberbullying for Primary School Students
Main Article Content
Abstract
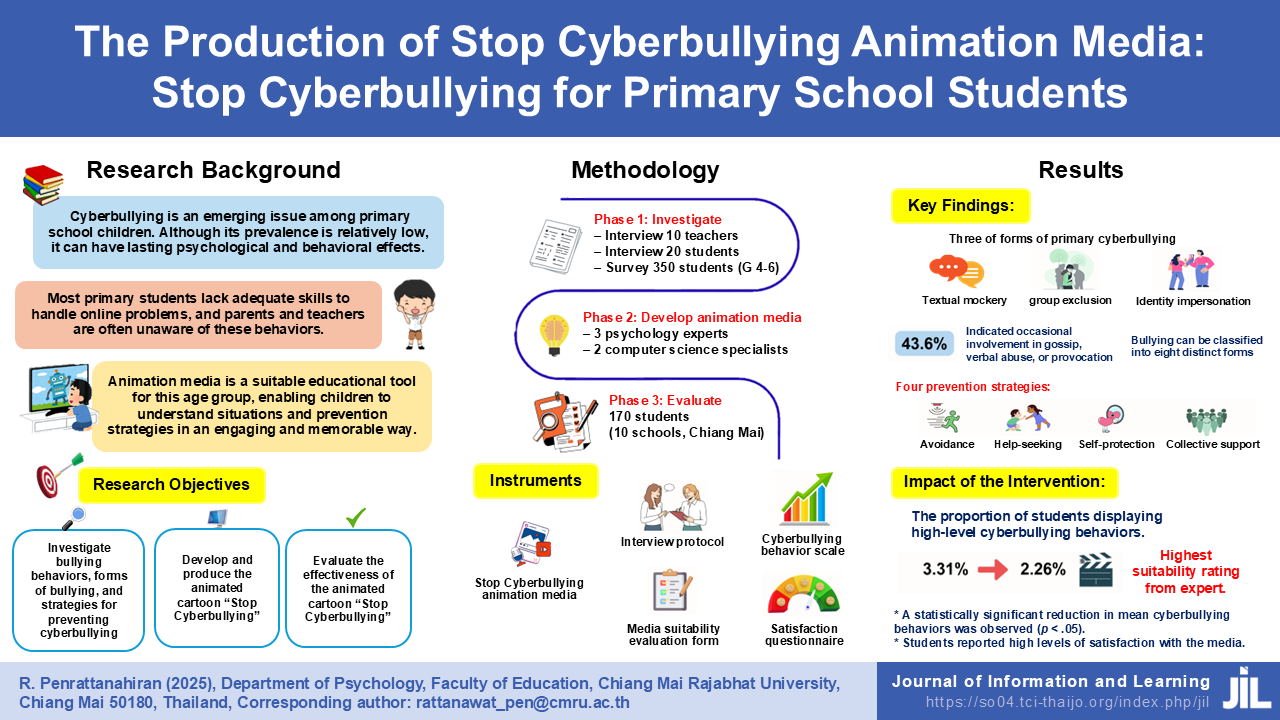
This research was conducted in three-phase: 1) data collection through interviews of 10 teachers and 20 students, plus a survey of 350 primary students (grades 4-6), 2) media development by 3 experts in psychology and 2 in computer, and 3) intervention implementation with 170 students across 10 Chiang Mai schools. Research instruments included interview protocols, behavioral assessment scales, "Stop Cyberbullying" animated media, evaluation forms, and satisfaction questionnaires. Data analysis utilized descriptive statistics, content analysis, and pre-post comparisons. The research findings revealed that: 1) There were three of forms of primary cyberbullying—textual mockery, group exclusion and identity impersonation. While the majority of students had never exhibited such behaviors, 43.6% indicated occasional involvement in gossip, verbal abuse, or provocation. Bullying can be classified into eight distinct forms and four preventive strategies have been identified: avoidance, help-seeking, self-protection, and collective support. 2) The developed animated cartoon media received the highest level of appropriateness rating. 3) Post-intervention results showed significant reduction in the level of cyberbullying behaviors (3.31% to 2.26%, p < .05) and a high level of satisfaction among students.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
The Journal of Information and Learning is operated by the Office of Academic Resources, Prince of Songkla University. All articles published in the journal are protected by Thailand copyright law. This copyright covers the exclusive rights to share, reproduce and distribute the article, including in electronic forms, reprints, translations, photographic reproductions, or similar. Authors own copyrights in the works they have created as well as the Office of Academic Resources. The Journal reserves the right to edit the language of papers accepted for publication for clarity and correctness, as well as to make formal changes to ensure compliance with the journal's guidelines. All authors must take public responsibility for the content of their paper.
References
Arif, A., Qadir, M. A., Martins, R. S., & Ahmed Khuwaja, H. M. (2024). The impact of cyberbullying on mental health outcomes amongst university students: A systematic review. PLOS Mental Health, 1(6), Article e0000166. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmen.0000166
Bandura, A. (1977). Social learning theory. Englewood Cliffs.
Bland, T., Guo, M., & Dousay, T. A. (2024). Multimedia design for learner interest and achievement: A visual guide to pharmacology. BMC Medical Education, 24(1), Article 113. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-024-05077-y
Chainwong, P., Skulphan, S., & Thapinta, D. (2020). Being cyberbullied and suicide risk among youths. The Journal of Psychiatric Nursing and Mental Health, 34(3), 133–151. https://he02.tci-thaijo.org/index.php/JPNMH/article/view/241401
Chicote-Beato, M., González-Víllora, S., Bodoque-Osma, A., & Olivas, R. (2024). Cyberbullying intervention and prevention programmes in Primary Education (6 to 12 years): A systematic review. Aggression and Violent Behavior, 77, Article 101938. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.avb.2024.101938
Child and Youth Media Institute. (2018). Cyberbullying. Natchawat.
Chureemas, R., & Poksupphiboon, A. (2024). Using animation media to enhance digital citizenship education: Developing and validating educational content for Bangkok students. Proceedings of the 5th Kyoto Conference on Arts Media & Culture, 35–40. https://doi.org/10.22492/issn.2436-0503.2024.4
Désiron, J., & Schneider, S. (2024). Exploring the interplay of information relevance and colorfulness in multimedia learning. Frontiers in Psychology, 15, Article 1393113. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1393113
Doane, A. N., Kelley, M. L., & Pearson, M. R. (2016). Reducing cyberbullying: A theory of reasoned action based video prevention program for college students. Aggressive Behavior, 42(2), 136–146. https://doi.org/10.1002/ab.21610
Fonseca, J., & Borges-Tiago, T. (2024). Digital literacy education and cyberbullying combat: Scope and perspectives. In: A. Kavoura, T. Borges-Tiago, & F. Tiago (Eds), Strategic innovative marketing and tourism. ICSIMAT 2023. Springer Proceedings in Business and Economics. Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-51038-0_18
Ginting, R. M., & Sahlepi, M. A. (2024). The impact of cyberbullying on adolescents on social media. International Journal of Sociology and Law, 1(2), 95–105. https://doi.org/10.62951/ijsl.v1i2.53
Hinduja, S., & Patchin, J. W. (2014). Bullying beyond the schoolyard: Preventing and responding to cyberbullying. Corwin press.
Hinduja, S., & Patchin, J. W. (2018). Cyberbullying: An update and synthesis of the research. In Handbook of bullying in schools: An international perspective (pp. 249-260). Routledge.
Inthanon, S. (2018). Cyberbullying. Child and Youth Media Institute.
Kohlberg, L. (1984). The philosophy of moral development: Moral stages and the idea of justice. Harper & Row.
Kreslavskaya, T. A. (2024). Psychological and pedagogical potential of animation in the education of primary school students: Analysis of modern approaches. Primary Education, 12(4), 26–31. https://doi.org/10.12737/1998-0728-2024-12-4-26-31
Kumari, K., & Yadav, R. K. (2024). The impact of cyberbullying on adolescents: Defining characteristics, consequences, and prevention strategies. International Journal For Multidisciplinary Research, 6(1), Article IJFMR240113915. https://doi.org/10.36948/ijfmr.2024.v06i01.13915
Kyshtymova, I., & Skorova, L. V. (2021). Psychological media competence: Basic content and structure. Integrative Psychological and Behavioral Science, 58, 771–785. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12124-021-09611-1
Lareki, A., Altuna, J., & Martínez-de-Morentin, J. I. (2023). Fake digital identity and cyberbullying. Media, Culture & Society, 45(2), 338–353. https://doi.org/10.1177/01634437221126081
Lertratthamrongkul, W. (2021). Cyberbullying among secondary school students: Prevalence, problem solving and risk behaviors. NEUARJ NEU Academic and Research Journal, 11(1), 275–289. https://so04.tci-thaijo.org/index.php/neuarj/article/view/249043
Li, C. (2024). A study of the application of educational psychology to educational practice. Communications in Humanities Research, 46, 7–11. https://doi.org/10.54254/2753-7064/46/20242271
Livazović, G., & Ham, E. (2019). Cyberbullying and emotional distress in adolescents: The importance of family, peers and school. Heliyon, 5(6), Article e01992. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e01992
Lukács J, Á., Takács, J., Soósné Kiss, Z., Kapitány-Fövény, M., Falus, A., & Feith, H. J. (2023). The effects of a cyberbullying intervention programme among primary school students. Child & Youth Care Forum, 52, 893–911. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10566-022-09714-9
Mameli, C., Menabò, L., Brighi, A., Menin, D., Culbert, C., Hamilton, J., Scheithauer, H., Smith, P., Völlink, T., Willems, R., Purdy, N., & Guarini, A. (2022). Stay safe and strong: Characteristics, roles and emotions of student-produced comics related to cyberbullying. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(14), Article 8776. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19148776
Martzoukou, K. (2022). “Maddie is online”: An educational video cartoon series on digital literacy and resilience for children. Journal of Research in Innovative Teaching & Learning, 15(1), 64–82. https://doi.org/10.1108/jrit-06-2020-0031
Mashlahah, A. U., Febriyana, N. H., & Najiha, N. (2024). Leveraging the animated video Ibra Berkisah to prevent bullying in early childhood. ThufuLA: Jurnal Inovasi Pendidikan Guru Raudhatul Athfal, 12(2), 329–344. https://doi.org/10.21043/thufula.v12i2.28939
Oktaviana, D. L., Rusnilawati. (2022). Role playing with digital comics in preventing bullying and cyberbullying behavior in elementary school. Jurnal Ilmiah Sekolah Dasar, 6(4), 603–609. https://doi.org/10.23887/jisd.v6i4.53685
Penrattanahiran R. (2021). Psychology for teachers. Chiang Mai Rajabhat University.
Saba, P., Qi, H., Saleem, A., Chen, I. J., Kausar, F. N., & Iqbal, M. F. (2023). Effects of animated movies on the aggression and behavior performance of primary school students and their control using a cognitive behavioral anger-control training (CBACT) program. Behavioral Sciences, 13(8), Article 659. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs13080659
Saracho, O. (2021). Theories of child development and their impact on early childhood education and care. Early Childhood Education Journal, 51, 15–30. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10643-021-01271-5
Slonje, R., & Smith, P. (2008). Cyberbullying: Another main type of bullying? Scandinavian Journal of Psychology, 49(2), 147–54. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-9450.2007.00611.x
Smith, P., Mahdavi, J., Carvalho, M., Fisher, S., Russell, S., & Tippett, N. (2008). Cyberbullying: Its nature and impact in secondary school pupils. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, and Allied Disciplines, 49(4), 376–85. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-7610.2007.01846.x
Thai Health Official. (2020, January 10). Phrưttikam būn lī dek Thai tit ʻandap 2 khō̜ng lōk [Thai children's bullying behavior ranks 2nd in the world]. https://www.thaihealth.or.th/?p=221002
Zamzami, M. R. A., & Zamzami, M. A. (2023). Designing teaching activity: Employing cartoon videos to improveyoung learners’ vocabulary. Pioneer: Journal of Language and Literature, 15(1), 102–118. https://doi.org/10.36841/pioneer.v15i1.2849
Zhang, W., Huang, S., Lam, L., Evans, R., & Zhu, C. (2022). Cyberbullying definitions and measurements in children and adolescents: Summarizing 20 years of global efforts. Frontiers in Public Health, 10, Article 1000504. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2022.1000504
Zhu, C., Huang, S., Evans, R., & Zhang, W. (2021). Cyberbullying among adolescents and children: A comprehensive review of the global situation, risk factors, and preventive measures. Frontiers in Public Health, 9, Article 634909. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2021.634909